Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus and Avian Metapneumovirus: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 39861016
- PMCID: PMC11769561
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens14010055
Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus and Avian Metapneumovirus: A Comprehensive Review
Erratum in
-
Correction: Mo, J.; Mo, J. Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus and Avian Metapneumovirus: A Comprehensive Review. Pathogens 2025, 14, 55.Pathogens. 2025 May 19;14(5):497. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14050497. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40430831 Free PMC article.
Abstract
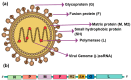
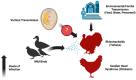
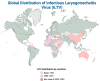
Respiratory avian viral diseases significantly impact the world poultry sector, leading to notable economic losses. The highly contagious DNA virus, infectious laryngotracheitis virus, and the RNA virus, avian metapneumovirus, are well known for their prevalent effects on avian respiratory systems. The infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV), stemming from the Herpesviridae family, manifests as an upper respiratory disease within birds. Characterized by acute respiratory signs, it sporadically emerges worldwide, presenting a persistent threat to poultry health. Avian metapneumovirus (aMPV), belonging to the Pneumoviridae family is identified as the cause behind severe rhinotracheitis in turkeys and swollen head syndrome in chickens. This disease can lead to heightened mortality rates, especially when coupled with secondary bacterial infections. This review offers a comprehensive analysis and understanding of the general properties of these specific avian respiratory viruses, control measures, and their global status.
Keywords: avian metapneumovirus; herpesvirus; infectious laryngotracheitis virus; pneumovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

