Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Neuroinflammation Intervention with Medicinal Plants: A Critical and Narrative Review of the Current Literature
- PMID: 39861194
- PMCID: PMC11768729
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18010133
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Neuroinflammation Intervention with Medicinal Plants: A Critical and Narrative Review of the Current Literature
Abstract
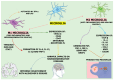
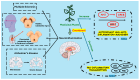
Neuroinflammation is a key factor in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, driven by the dysregulation of molecular pathways and activation of the brain's immune system, resulting in the release of pro-inflammatory and oxidative molecules. This chronic inflammation is exacerbated by peripheral leukocyte infiltration into the central nervous system. Medicinal plants, with their historical use in traditional medicine, have emerged as promising candidates to mitigate neuroinflammation and offer a sustainable alternative for addressing neurodegenerative conditions in a green healthcare framework. This review evaluates the effects of medicinal plants on neuroinflammation, emphasizing their mechanisms of action, effective dosages, and clinical implications, based on a systematic search of databases such as PubMed, SCOPUS, and Web of Science. The key findings highlight that plants like Cleistocalyx nervosum var. paniala, Curcuma longa, Cannabis sativa, and Dioscorea nipponica reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β), inhibit enzymes (COX-2 and iNOS), and activate antioxidant pathways, particularly Nrf2. NF-κB emerged as the primary pro-inflammatory pathway inhibited across studies. While the anti-inflammatory potential of these plants is significant, the variability in dosages and phytochemical compositions limits clinical translation. Here, we highlight that medicinal plants are effective modulators of neuroinflammation, underscoring their therapeutic potential. Future research should focus on animal models, standardized protocols, and safety assessments, integrating advanced methodologies, such as genetic studies and nanotechnology, to enhance their applicability in neurodegenerative disease management.
Keywords: Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT); NLRP3 inflammasome; medicinal plants; microglia; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroinflammation; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2); nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB); oxidative stress; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pan T., Xiao Q., Fan H.J., Xu L., Qin S.C., Yang L.X., Jin X.M., Xiao B.G., Zhang B., Ma C.G., et al. Wuzi Yanzong Pill relieves MPTP-induced motor dysfunction and neuron loss by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023;38:2211–2222. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01266-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

