Differential Enhancement of Fat-Soluble Vitamin Absorption and Bioefficacy via Micellization in Combination with Selected Plant Extracts In Vitro
- PMID: 39861489
- PMCID: PMC11769215
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17020359
Differential Enhancement of Fat-Soluble Vitamin Absorption and Bioefficacy via Micellization in Combination with Selected Plant Extracts In Vitro
Abstract
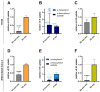
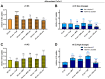
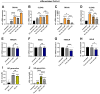
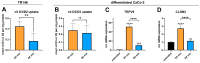
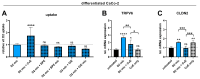
Background/Objectives: Individuals with special metabolic demands are at risk of deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins, which can be counteracted via supplementation. Here, we tested the ability of micellization alone or in combination with selected natural plant extracts to increase the intestinal absorption and bioefficacy of fat-soluble vitamins. Methods: Micellated and nonmicellated vitamins D3 (cholecalciferol), D2 (ergocalciferol), E (alpha tocopheryl acetate), and K2 (menaquionone-7) were tested in intestinal Caco-2 or buccal TR146 cells in combination with curcuma (Curcuma longa), black pepper (Piper nigrum), or ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) plant extracts. The vitamin uptake was quantified via HPLC-MS, and bioefficacy was assessed via gene expression analyses or the Griess assay for nitric oxide generation. Results: Micellization increased the uptake of vitamin D into buccal and intestinal cells, with vitamin D3 being more efficient than vitamin D2 in increasing the expression of genes involved in calcium transport. The micellization of vitamin E acetate increased its uptake and conversion into biologically active free vitamin E in intestinal cells only. The vitamin K2 uptake into buccal and intestinal cells was increased via micellization. Plant extracts increased the uptake of select micellated vitamins, with no plant extract being effective in combination with all vitamins. The curcuma extract increased the uptake of vitamins D2/D3 but not their bioefficacy. Black pepper and ginger extracts increased the uptake of vitamin E acetate into intestinal cells but failed to increase its conversion into free vitamin E. The ginger extract augmented the uptake of vitamin K2 and increased NO generation additively. Conclusions: Our data substantiate the positive effects of micellization on fat-soluble vitamin absorption and bioefficacy in vitro. While the application of plant extracts in addition to micellization to further increase bioefficacy is an interesting approach, further studies are warranted to understand vitamin-specific interactions and translation into increased bioefficacy.
Keywords: alpha tocopherol acetate; bioavailability; buccal absorption; cholecalciferol; ergocalciferol; intestinal absorption; intestinal bioefficacy; menaquinone-7; micellization; vitamin–plant–compound interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Stefanie Steinbauer, Melanie Wallner, Theresa Gramatte, Julian Weghuber and Bernhard Blank-Landeshammer were employed by the company FFoQSI GmbH—Austrian Competence Centre for Feed and Food Quality, Safety and Innovation. M.I. is employed by PM International AG, which provided funding for the Austrian Competence Centre for Feed and Food Quality, Safety and Innovation and the Josef Ressel Center for Phytogenic Drug Research. PM International AG had no influence on the study design or the decision to report the research. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Desmarchelier C., Borel P., Goncalves A., Kopec R., Nowicki M., Morange S., Lesavre N., Portugal H., Reboul E. A Combination of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Is Associated with Interindividual Variability in Cholecalciferol Bioavailability in Healthy Men. J. Nutr. 2016;146:2421–2428. doi: 10.3945/jn.116.237115. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

