Comparative Analysis of Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity in the Leaves of Invasive Amelanchier × spicata (Lam.) K. Koch in Lithuania
- PMID: 39861574
- PMCID: PMC11769043
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14020221
Comparative Analysis of Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity in the Leaves of Invasive Amelanchier × spicata (Lam.) K. Koch in Lithuania
Abstract
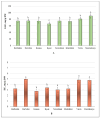
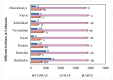
The environmental impact of invasive species necessitates creating a strategy for managing their spread by utilising them as a source of potentially high-value raw materials. Amelanchier × spicata (Lam.) K. Koch (dwarf serviceberry) is a shrub species in the Rosaceae Juss. family. The evaluation of different populations of plants that accumulate great amounts of biologically active compounds is requisite for the quality determination of plant materials and medicinal and nutritional products. The assessment of natural resources from a phytogeographic point of view is relevant. Phytochemical analysis of A. spicata leaf samples was carried out using spectrophotometric methods, HPLC-PDA, and HPLC-MS techniques, while antioxidant activity was determined using ABTS, FRAP, and CUPRAC assays. A significant diversification of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity was determined in the A. spicata leaf samples collected in different habitats. Due to their characteristic chemical heterogeneity, natural habitats lead to the diversity of indicators characterising the quality of plant raw materials. Chlorogenic acid and neochlorogenic acid, as well as quercitrin, rutin, and hyperoside, were found to be predominant among the phenolic compounds. Thus, these compounds can be considered phytochemical markers, characteristic of the A. spicata leaf material from northern Europe.
Keywords: Amelanchier × spicata; antioxidant activity; dwarf serviceberry; invasive plant; phenolics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bogoslovskaya E.R., Vinogradova Y., Molkanova O., Hussien M. Anatomical Structures of Saskatoon Berry (Amelanchier Medik.) Leaves Under Different Cultivation Conditions. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 2023;30:185–193. doi: 10.3329/bjpt.v30i2.70495. - DOI
-
- Szpadzik E., Krupa T. The Yield, Fruit Quality and Some of Nutraceutical Characteristics of Saskatoon Berries (Amelanchier alnifolia Nutt.) in the Conditions of Eastern Poland. Agriculture. 2021;11:824. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11090824. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

