Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS): Transition from Liquid to Solid-A Comprehensive Review of Formulation, Characterization, Applications, and Future Trends
- PMID: 39861711
- PMCID: PMC11768142
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010063
Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS): Transition from Liquid to Solid-A Comprehensive Review of Formulation, Characterization, Applications, and Future Trends
Abstract
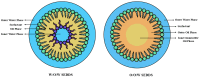
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) represent an innovative approach to improving the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs, addressing significant challenges associated with oral drug delivery. This review highlights the advancements and applications of SEDDS, including their transition from liquid to solid forms, while addressing the formulation strategies, characterization techniques, and future prospects in pharmaceutical sciences. The review systematically analyzes existing studies on SEDDS, focusing on their classification into liquid and solid forms and their preparation methods, including spray drying, hot-melt extrusion, and adsorption onto carriers. Characterization techniques such as droplet size analysis, dissolution studies, and solid-state evaluations are detailed. Additionally, emerging trends, including 3D printing, hybrid systems, and supersaturable SEDDS (Su-SEDDS), are explored. Liquid SEDDS (L-SEDDS) enhance drug solubility and absorption by forming emulsions upon contact with gastrointestinal fluids. However, they suffer from stability and leakage issues. Transitioning to solid SEDDS (S-SEDDS) has resolved these limitations, offering enhanced stability, scalability, and patient compliance. Innovations such as personalized 3D-printed SEDDS, biologics delivery, and targeted systems demonstrate their potential for diverse therapeutic applications. Computational modeling and in silico approaches further accelerate formulation optimization. SEDDS have revolutionized drug delivery by improving bioavailability and enabling precise, patient-centric therapies. While challenges such as scalability and excipient toxicity persist, emerging technologies and multidisciplinary collaborations are paving the way for next-generation SEDDS. Their adaptability and potential for personalized medicine solidify their role as a cornerstone in modern pharmaceutical development.
Keywords: 3D printing; SEDDS; SNEDDS; bioavailability enhancement; hot-melt extrusion; in silico modeling; lipid-based drug delivery systems; personalized medicine; self-emulsifying drug delivery systems; solid SEDDS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tran P., Park J.-S. Recent Trends of Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System for Enhancing the Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021;51:439–463. doi: 10.1007/s40005-021-00516-0. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

