Advances in Pure Drug Self-Assembled Nanosystems: A Novel Strategy for Combined Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 39861716
- PMCID: PMC11768559
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010068
Advances in Pure Drug Self-Assembled Nanosystems: A Novel Strategy for Combined Cancer Therapy
Abstract
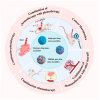
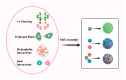
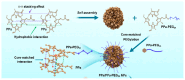
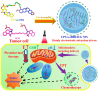
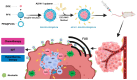
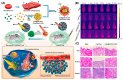
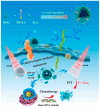
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems hold great promise for improving the effectiveness of anti-tumor therapies. However, their clinical translation remains hindered by several significant challenges, including intricate preparation processes, limited drug loading capacity, and concerns regarding potential toxicity. In this context, pure drug-assembled nanosystems (PDANSs) have emerged as a promising alternative, attracting extensive research interest due to their simple preparation methods, high drug loading efficiency, and suitability for large-scale industrial production. This innovative approach presents new opportunities to enhance both the safety and therapeutic efficacy of cancer treatments. This review comprehensively explores recent progress in the application of PDANSs for cancer therapy. It begins by detailing the self-assembly mechanisms and fundamental principles underlying PDANS formation. The discussion then advances to strategies for assembling single pure drug nanoparticles, as well as the co-assembly of multiple drugs. Subsequently, the review addresses the therapeutic potential of PDANSs in combination treatment modalities, encompassing diagnostic and therapeutic applications. These include combinations of chemotherapeutic agents, phototherapeutic approaches, the integration of chemotherapy with phototherapy, and the synergistic use of immunotherapy with other treatment methods. Finally, the review highlights the potential of PDANSs in advancing tumor therapy and their prospects for clinical application, providing key insights for future research aimed at optimizing this technology and broadening its utility in cancer treatment.
Keywords: cancer therapy; carrier-free; combination treatment; nanosystems; pure drug; self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

