Current Status of Gout Arthritis: Current Approaches to Gout Arthritis Treatment: Nanoparticles Delivery Systems Approach
- PMID: 39861750
- PMCID: PMC11768112
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010102
Current Status of Gout Arthritis: Current Approaches to Gout Arthritis Treatment: Nanoparticles Delivery Systems Approach
Abstract
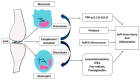
The deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals within joint spaces produces a painful inflammatory condition known as gout, a specific form of arthritis. The condition calls for a combined curative and preventive management model. A new development in the approach to gout is that of NLRP3-targeted biologic agents, such as monoclonal therapies, to provide more accurate treatment by blocking specific pro-inflammatory cytokines. Nanoparticle drug delivery enhances biological availability and delivery to targets, which may increase therapeutic efficacy and decrease general toxicity. The preventive approach again cannot be ignored, mainly keeping up certain modifications in diet and weight, along with pharmacological therapies to reduce uric acid (UA) levels and to decrease the frequency of acute attacks. The advancement of genetic profiling of patients and biomarker discoveries drives the trend towards building individualized medicine and care, quickly gaining ground as the most effective method of delivering treatments to individual patients, moving away from one-size-fits-all treatments. The following paper aims to provide an updated account of the management of gout with a focus on recent developments, in order to enhance these approaches, the quality of life for patients with gout, and the standard of gout treatment.
Keywords: lifestyle modification; nanoparticle delivery systems; preventive approach; quality of life; uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limitations of the Current Standards of Care for Treating Gout and Crystal Deposition in the Primary Care Setting: A Review.Clin Ther. 2017 Feb;39(2):430-441. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28089200 Review.
-
Overview of Serum Uric Acid Treatment Targets in Gout: Why Less Than 6 mg/dL?Postgrad Med. 2016 Sep;128(7):706-15. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2016.1221732. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Postgrad Med. 2016. PMID: 27558643 Review.
-
Natural Products as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Gout.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 16;13:861399. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.861399. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystal arthritides - gout and calcium pyrophosphate arthritis : Part 2: clinical features, diagnosis and differential diagnostics.Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018 Jul;51(5):579-584. doi: 10.1007/s00391-017-1198-2. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018. PMID: 28233118 Review. English.
-
Gout: epitome of painful arthritis.Metabolism. 2010 Oct;59 Suppl 1:S32-6. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2010.07.009. Metabolism. 2010. PMID: 20837191 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the role of cell signaling pathways in gout pathogenesis and the therapeutic potential of phytoconstituents in their modulation.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May;33(5):2307-2323. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01741-x. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40249480 Review.
-
The Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Coronary Heart Disease in Patients With Gout: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2025 Jun 1;17(6):e85194. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85194. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40458383 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism Prediction of Sinomenine Based on Network Pharmacology and Its Biological Activity Verification.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 13;14(5):543. doi: 10.3390/biology14050543. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427732 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources