CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Detects Neuroinflammation in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy with High Accuracy
- PMID: 39861878
- PMCID: PMC11768778
- DOI: 10.3390/v17010089
CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Detects Neuroinflammation in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy with High Accuracy
Abstract
Background and objectives: HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM) is a chronic progressive inflammatory disease of the spinal cord. This study assesses the diagnostic accuracy of the neuroinflammatory biomarkers neopterin and cysteine-X-cysteine motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL-10) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for HAM.
Methods: CSF samples from 75 patients with neurological disorders-33 with HAM (Group A), 19 HTLV-1-seronegative with other neuroinflammatory diseases (Group B), and 23 HTLV-1-seronegative with non-neuroinflammatory diseases (Group C)-were retrospectively evaluated. CSF examination included routine analysis, neopterin, and CXCL-10. The diagnostic potential of the biomarkers was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curves.
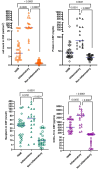
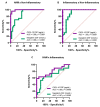
Results: Higher white cell counts and concentrations of protein, neopterin, and CXCL-10 in CSF were detected in group A (patients with HAM) and group B (p < 0.05). Neopterin showed good accuracy for HAM (A) (cut-off 15 nmol/L, 80% sensitivity, 74% specificity) and other neuroinflammation (group B) (cut-off 20 nmol/L, 79% sensitivity, 83% specificity). CXCL-10 demonstrated the highest accuracy in both groups, with Group A (cut-off 110 pg/mL, 97% sensitivity, 96% specificity) and Group B (cut-off 220 pg/mL, 100% sensitivity, 100% specificity).
Conclusions: Neopterin and CXCL-10 in CSF are accurate biomarkers for detecting neuroinflammation, including HAM. CXCL-10, in particular, is the superior biomarker for both chronic and acute neuroinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: CXCL-10; HTLV-1-associated myelopathy; accuracy; biomarker; cerebrospinal fluid; diagnosis; neopterin.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Poiesz B.J., Ruscetti F.W., Gazdar A.F., Bunn P.A., Minna J.D., Gallo R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1980;77:7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

