Protocol for alleviating alcohol-induced conditioned place preference in mice using alternating bilateral sensory stimulation
- PMID: 39862433
- PMCID: PMC11804109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.103596
Protocol for alleviating alcohol-induced conditioned place preference in mice using alternating bilateral sensory stimulation
Abstract
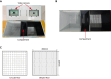
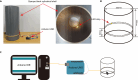
Alternating bilateral sensory stimulation (ABS) is a clinical physical therapy technique effective in treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). However, its utilization in treating conditions beyond PTSD remains limited. Here, we present a protocol to reduce ethanol-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) using 4 Hz ABS. We describe steps for the assembly of ABS apparatus, CPP training, and ABS treatment. This protocol has been validated in male mice and can be used to explore the mechanism behind the therapeutic effect of ABS. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Lei et al.1.
Keywords: Behavior; Health Sciences; Model Organisms; Neuroscience.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Markus W., Hornsveld H.K., Burk W.J., de Weert-van Oene G.H., Becker E.S., DeJong C.A.J. Addiction-Focused Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing Therapy as an Adjunct to Regular Outpatient Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder: Results From a Randomized Clinical Trial. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2020;44:272–283. doi: 10.1111/acer.14249. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

