Downregulation of the phosphatase PHLPP1 contributes to NNK-induced malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs)
- PMID: 39863100
- PMCID: PMC11889559
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108221
Downregulation of the phosphatase PHLPP1 contributes to NNK-induced malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs)
Abstract
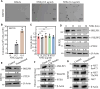
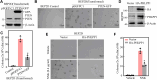
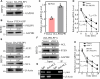
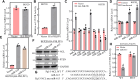
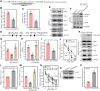
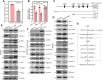
Cigarette smoking (CS) is one of the greatest health concerns, which can cause lung cancer. 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), a tobacco-specific nitrosamine, has been well-documented for its carcinogenic activity in both epidemiological and laboratory studies. PH domain leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase 1 (PHLPP1) and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) are two well-known phosphatase tumor suppressors that have been reported to be downregulated in human lung cancer tissues. However, the effect of NNK exposure on the expression of PHLPP1 and PTEN is unknown, and such effects may be early events leading to lung carcinogenesis. We explored this question in current studies and found that exposure of human bronchial epithelial BEP2D cells to NNK resulted in cell malignant transformation accompanied by a remarkable downregulation of PHLPP1 and PTEN. Such downregulation of PHLPP1 and PTEN was also consistently observed in vivo in Cigarette Smoking-exposed mouse lung tissues. Our studies further showed that overexpression of PHLPP1 or PTEN alleviated NNK-induced BEP2D cell transformation. Ectopic expression of PHLPP1 promoted PTEN protein expression, while PTEN overexpression did not affect PHLPP1 expression. Mechanistic studies showed that NNK was able to inhibit PP2A-C activity, which directly attenuated c-Jun phosphorylation at Ser63/73, and subsequently inhibited the PHLPP1 transcription and expression. Further, the downregulation of PHLPP1 led to a reduction of pten mRNA stability and expression through the HUR/Jun D/miR-613/NCL axis. Taken together, our studies advance the field of tobacco-induced lung cancer research by uncovering new mechanistic insights and identifying a novel molecular axis that could inform future therapeutic strategies. It also adds a new dimension by exploring the interaction between PHLPP1 and PTEN in the context of tobacco carcinogen exposure.
Keywords: NNK; PHLPP1; PP2AC; PTEN; lung carcinogenesis; miR-613.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p27 specifically decreases in squamous carcinoma, and mediates NNK-induced transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Aug;28(15):e18577. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18577. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39099000 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal effects of NNK and SLURP-1 on oncogene expression in target epithelial cells.Life Sci. 2012 Nov 27;91(21-22):1122-5. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.02.004. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22369755 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MEG3 downregulation mediated by DNMT3b contributes to nickel malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells via modulating PHLPP1 transcription and HIF-1α translation.Oncogene. 2017 Jul 6;36(27):3878-3889. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.14. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28263966 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding tobacco smoke carcinogen NNK and lung tumorigenesis.Int J Oncol. 2006 Oct;29(4):745-52. Int J Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16964372 Review.
-
Tobacco carcinogen NNK-induced lung cancer animal models and associated carcinogenic mechanisms.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015 Jul;47(7):477-87. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv041. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015. PMID: 26040315 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

