The juxtamembrane sequence of small ankyrin 1 mediates the binding of its cytoplasmic domain to SERCA1 and is required for inhibitory activity
- PMID: 39863105
- PMCID: PMC11927728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108216
The juxtamembrane sequence of small ankyrin 1 mediates the binding of its cytoplasmic domain to SERCA1 and is required for inhibitory activity
Abstract
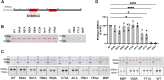
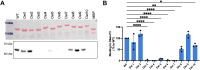
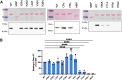
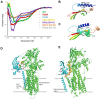
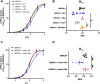
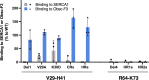
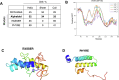
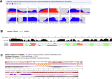
Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase1 (SERCA1) is responsible for the clearance of cytosolic Ca2+ in skeletal muscle. Due to its vital importance in regulating Ca2+ homeostasis, the regulation of SERCA1 has been intensively studied. Small ankyrin 1 (sAnk1, Ank1.5), a 17 kDa muscle-specific isoform of ANK1, binds to SERCA1 directly via both its transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains and inhibits SERCA1's ATPase activity. Here, we characterize the interaction between the cytoplasmic domain of sAnk1 (sAnk1(29-155)) and SERCA1. The binding affinity for sAnk1 (29-155) to SERCA1 was 444 nM by blot overlay, about 7-fold weaker than the binding of sAnk1(29-155) to obscurin, a giant protein of the muscle cytoskeleton. Site-directed mutagenesis identified K38, H39, and H41, in the juxtamembrane region, as residues likely to mediate binding to SERCA1. These residues are not required for obscurin binding. Residues R64-K73, which do contribute to obscurin binding, are also required for binding to SERCA1, but only the hydrophobic residues in this sequence are required, not the positively charged residues necessary for obscurin binding. Circular dichroism analysis of sAnk1(29-155) indicates that most mutants show significant structural changes, with the exception of those containing alanines in place of K38, H39 and H41. Although the cytoplasmic domain of sAnk1 does not inhibit SERCA1's Ca2+-ATPase activity, with or without mutations in the juxtamembrane sequence, the inhibitory activity of full-length sAnk1 requires the WT juxtamembrane sequence. We used these data to model sAnk1 and the sAnk1-SERCA1 complex. Our results suggest that, in addition to its transmembrane domain, sAnk1 uses its juxtamembrane sequence and perhaps part of its obscurin binding site to bind to SERCA1, and that this binding contributes to their robust association in situ, as well as regulation of SERCA1's activity.
Keywords: AlphaFold; Ca-ATPase; ankyrin; circular dichroism (CD); complex; membrane transport; sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR); skeletal muscle; structural model.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification of Small Ankyrin 1 as a Novel Sarco(endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 1 (SERCA1) Regulatory Protein in Skeletal Muscle.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 13;290(46):27854-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.676585. Epub 2015 Sep 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26405035 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic interactions mediate binding of obscurin to small ankyrin 1: biochemical and molecular modeling studies.J Mol Biol. 2011 Apr 29;408(2):321-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.01.053. Epub 2011 Feb 17. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21333652 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between small ankyrin 1 and sarcolipin coordinately regulate activity of the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA1).J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 30;292(26):10961-10972. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.783613. Epub 2017 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28487373 Free PMC article.
-
Organization of junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum proteins in skeletal muscle fibers.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015 Dec;36(6):501-15. doi: 10.1007/s10974-015-9421-5. Epub 2015 Sep 15. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015. PMID: 26374336 Review.
-
Age-related chemical modification of the skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase of the rat.Mech Ageing Dev. 1999 Mar 15;107(3):221-31. doi: 10.1016/s0047-6374(98)00158-4. Mech Ageing Dev. 1999. PMID: 10360678 Review.
References
-
- Primeau J.O., Armanious G.P., Fisher M.E., Young H.S. The SarcoEndoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase. Subcell. Biochem. 2018;87:229–258. - PubMed
-
- Lipskaia L., Hulot J.S., Lompre A.M. Role of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium content and calcium ATPase activity in the control of cell growth and proliferation. Pflugers Arch. 2009;457:673–685. - PubMed
-
- Periasamy M., Maurya S.K., Sahoo S.K., Singh S., Sahoo S.K., Reis F.C.G., et al. Role of SERCA pump in muscle thermogenesis and metabolism. Compr. Physiol. 2017;7:879–890. - PubMed
-
- Gamu D., Juracic E.S., Hall K.J., Tupling A.R. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and SERCA: a nexus for muscular adaptive thermogenesis. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020;45:1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

