CHD6 has poly(ADP-ribose)- and DNA-binding domains and regulates PARP1/2-trapping inhibitor sensitivity via abasic site repair
- PMID: 39863586
- PMCID: PMC11762318
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56085-5
CHD6 has poly(ADP-ribose)- and DNA-binding domains and regulates PARP1/2-trapping inhibitor sensitivity via abasic site repair
Abstract
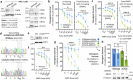
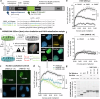
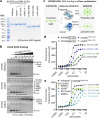
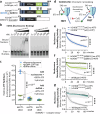
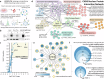
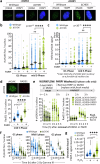
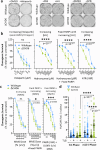
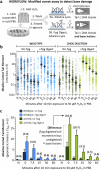
To tolerate oxidative stress, cells enable DNA repair responses often sensitive to poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymerase 1 and 2 (PARP1/2) inhibition-an intervention effective against cancers lacking BRCA1/2. Here, we demonstrate that mutating the CHD6 chromatin remodeler sensitizes cells to PARP1/2 inhibitors in a manner distinct from BRCA1, and that CHD6 recruitment to DNA damage requires cooperation between PAR- and DNA-binding domains essential for nucleosome sliding activity. CHD6 displays direct PAR-binding, interacts with PARP-1 and other PAR-associated proteins, and combined DNA- and PAR-binding loss eliminates CHD6 relocalization to DNA damage. While CHD6 loss does not impair RAD51 foci formation or DNA double-strand break repair, it causes sensitivity to replication stress, and PARP1/2-trapping or Pol ζ inhibitor-induced γH2AX foci accumulation in S-phase. DNA repair pathway screening reveals that CHD6 loss elicits insufficiency in apurinic-apyrimidinic endonuclease (APEX1) activity and genomic abasic site accumulation. We reveal APEX1-linked roles for CHD6 important for understanding PARP1/2-trapping inhibitor sensitivity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

