The α-globin super-enhancer acts in an orientation-dependent manner
- PMID: 39863595
- PMCID: PMC11762767
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56380-1
The α-globin super-enhancer acts in an orientation-dependent manner
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The α-globin super-enhancer acts in an orientation-dependent manner.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 19;16(1):2714. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58071-3. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40108171 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
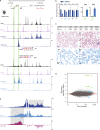
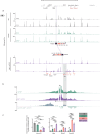
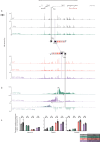
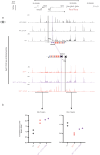
Individual enhancers are defined as short genomic regulatory elements, bound by transcription factors, and able to activate cell-specific gene expression at a distance, in an orientation-independent manner. Within mammalian genomes, enhancer-like elements may be found individually or within clusters referred to as locus control regions or super-enhancers (SEs). While these behave similarly to individual enhancers with respect to cell specificity, distribution and distance, their orientation-dependence has not been formally tested. Here, using the α-globin locus as a model, we show that while an individual enhancer works in an orientation-independent manner, the direction of activity of a SE changes with its orientation. When the SE is inverted within its normal chromosomal context, expression of its normal targets, the α-globin genes, is severely reduced and the normally silent genes lying upstream of the α-globin locus are upregulated. These findings add to our understanding of enhancer-promoter specificity that precisely activate transcription.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.R.H. is a founder and shareholder of Nucleome Therapeutics; J.R.H., and D.J.D. are paid consultants for Nucleome Therapeutics. J.R.H. holds patents for NG Capture-C. Patent applicant: Oxford University Innovation Limited, Name of inventor(s): James R Hughes and James Davies nos. WO2017068379A1, EP3365464B1 and US10934578B2. Specific aspect of manuscript covered in patent application: NG-Capture C experiments. These authors declare no other financial or non-financial interests. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Grosveld, F., van Staalduinen, J. & Stadhouders, R. Transcriptional Regulation by (Super)Enhancers: From Discovery to Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 10.1146/annurev-genom-122220-093818 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

