Poor fixation stability does not account for motion perception deficits in amblyopia
- PMID: 39863630
- PMCID: PMC11762986
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83624-9
Poor fixation stability does not account for motion perception deficits in amblyopia
Abstract
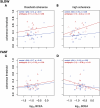
People with amblyopia show deficits in global motion perception, especially at slow speeds. These observers are also known to have unstable fixation when viewing stationary fixation targets, relative to healthy controls. It is possible that poor fixation stability during motion viewing interferes with the fidelity of the input to motion-sensitive neurons in visual cortex. To probe these mechanisms at a behavioral level, we assessed motion coherence thresholds in adults with amblyopia while measuring fixation stability. Consistent with prior work, participants with amblyopia had elevated coherence thresholds for the slow speed stimuli, but not the fast speed stimuli, using either the amblyopic or the fellow eye. Fixation stability was elevated in the amblyopic eye relative to controls across all motion stimuli, and not selective for conditions on which perceptual deficits were observed. Fixation stability was not related to visual acuity, nor did it predict coherence thresholds. These results suggest that motion perception deficits might not be a result of poor input to the motion processing system due to unstable fixation, but rather due to processing deficits in motion-sensitive visual areas.
Keywords: Amblyopia; Fixation stability; Global motion perception; Motion coherence; Speed.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

