Enhancing food and nutrition security in Himalayan foothills with neglected and underutilized millets
- PMID: 39863657
- PMCID: PMC11762736
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-85090-9
Enhancing food and nutrition security in Himalayan foothills with neglected and underutilized millets
Abstract
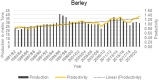
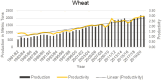
Global food production predominantly depends on a limited number of cereal crops; however, numerous other crops have the potential to support the nutrition and economy of many local communities in developing countries. The different crop species characterized as having relatively low perceived economic importance or agricultural significance are known as underutilized crops. Millet is one of the underutilized crops with significant potential to address nutrient and hunger-related challenges in many developing countries like Nepal due to its versatility and climate resilience. Little is known about the determinants of adoption, cultural importance, and nutritional benefits of millet. Therefore, this study uses data from 1988 to 2019 and examines trends in millet production and its climate resilience, employing the Dynamic Ordinary Least Square Method. Results indicate that fertilizer use, cultivated area, and rural population significantly impact millet production in Nepal, while mean temperature has a negative but insignificant effect. The findings suggest that climate change does not significantly impact millet production. Millet is well adapted to challenging environments and offers superior nutritional value, suggesting that integration of millet into modern agriculture could be a valuable tool for creating a more sustainable, equitable, resilient, and healthy agrifood system that benefits both people and the planet. This research provides valuable insights for policymakers to enhance underutilized crops such as millet and implement strategies to integrate them into central agrifood systems. It also has a more considerable socio-economic impact on local communities.
Keywords: Climate-resilient crops; Food security; Himalayan foothills; Millet potential; Nutrition security; Sustainable agriculture.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: Data used in this study is publicly available. It does not involve human subjects, and is not based on a survey or experiment. Further, the data is at the district level, and not at the individual or household level. Informed consent: This study uses secondary data and is not based on a survey or experiment. Human and animal rights: This study uses secondary data publicly available at the district level.
Figures



References
-
- IFAD. The state of food security and nutrition in the world 2017. Tech. Rep., IFAD, UNICEF, and others (2017).
-
- Khoury, C., Laliberté, B. & Guarino, L. Trends in ex situ conservation of plant genetic resources: a review of global crop and regional conservation strategies. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol.57, 625–639 (2010). - DOI
-
- Imathiu, S. Neglected and underutilized cultivated crops with respect to indigenous african leafy vegetables for food and nutrition security. J. Food Secur.9, 115–125 (2021). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

