Variations of renal Doppler indices during the initial 24-hour predict acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis: A single-center observational case-control clinical study
- PMID: 39864312
- PMCID: PMC11795832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100538
Variations of renal Doppler indices during the initial 24-hour predict acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis: A single-center observational case-control clinical study
Abstract
Background and objective: The aim of this retrospective observational case-control study was to examine the significance of different renal Doppler marker variations within the initial 24-hour period as potential predictors of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in patients with sepsis.
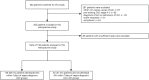
Methods: A total of 198 sepsis patients were enrolled and categorized into two groups: the AKI group (n = 136) and the non-AKI group (n = 62). Three renal Doppler indices, Renal Resistive Index (RRI), Power Doppler Ultrasound (PDU) score and Renal Venous Stasis Index (RVSI), were measured within 6h (T0) and at 24h (T1) after ICU admission.
Results: The AKI group had more hypertension patients than the non-AKI group (p = 0.047). The cases of the AKI group showed higher levels of CRP (p = 0.001), PCT (p < 0.001), lactate (p < 0.001), AST (p = 0.003), ALT (p = 0.049), total bilirubin (p = 0.034), BNP (p = 0.019) and cTnI (p = 0.012). The RRI at T1 was significantly higher in the AKI group (p = 0.037). AKI group exhibited a lower incidence of reduced RRI at T1 compared with non-AKI group (p < 0.001). After controlling for age, sex, and BMI through partial correlation analysis, the results indicated significant associations between SA-AKI and CVP (r = -0.473), SOFA score (r = 0.425), lactate (r = 0.378), and RRI reduction (r = -0.344) in sepsis patients. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that variables including CVP, SOFA score, CRP, lactate, VIS, and RRI not reduced following 24h of ICU treatment were predictive indicators for early detection of SA-AKI in sepsis patients.
Conclusion: CVP, SOFA score, CRP, lactate, VIS, and RRI not reduction following 24h of ICU treatment can be utilized as predictive indicators for early detection of SA-AKI in sepsis patients.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Initial 24-hour of icu administration; Prediction; Renal Doppler index; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
[Renal echography and cystatin C for prediction of acute kidney injury: very different in patients with cardiac failure or sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Oct;31(10):1258-1263. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.10.015. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31771725 Chinese.
-
Continuous renal replacement therapy with adsorbing filter oXiris in the treatment of sepsis associated acute kidney injury: a single-center retrospective observational study.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Dec 18;25(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03897-0. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39696043 Free PMC article.
-
[Value of the combination of renal resistive index and central venous pressure to predict septic shock induced acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Apr;32(4):473-477. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20191014-00062. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32527356 Chinese.
-
Predictive value of renal resistive index for the onset of acute kidney injury and its non-recovery: A systematic review and meta-analysis .Clin Nephrol. 2020 Apr;93(4):172-186. doi: 10.5414/CN109979. Clin Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32017700
-
Early Impact on Renal Parenchymal Vascularization of Chimney Grafts Versus Fenestrated Grafts.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016 May;51(5):647-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 26944599 Review.
References
-
- Citerio G., Bakker J., Bassetti M., Benoit D., Cecconi M., Curtis J.R., et al. Year in review in intensive care medicine 2013: I. Acute kidney injury, ultrasound, hemodynamics, cardiac arrest, transfusion, neurocritical care, and nutrition. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40(2):147–159. - PubMed
-
- Zhi H.J., Cui J., Yuan M.W., Zhao Y.N., Zhao X.W., Zhu T.T., et al. Predictive performance of renal resistive index, semiquantitative power Doppler ultrasound score and renal venous Doppler waveform pattern for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients and prediction model establishment: a prospective observational study. Ren Fail. 2023;45(2) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous