Accuracy of full arch scans performed with nine different scanning patterns- an in vitro study
- PMID: 39865140
- PMCID: PMC11769864
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-025-06154-2
Accuracy of full arch scans performed with nine different scanning patterns- an in vitro study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Accuracy of full arch scans performed with nine different scanning patterns- an in vitro study.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Feb 18;29(2):135. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06233-4. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 39964493 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Evaluation of the accuracy of direct digitization of maxillary scans depending on the scanning strategy.
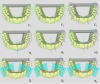
Materials and methods: A maxillary model with a metal bar as a reference structure fixed between the second molars was digitized using the CEREC Primescan AC scanner (N = 225 scans). Nine scanning strategies were selected (n = 25 scans per strategy), differing in scan area segmentation (F = full jaw, H = half jaw, S = sextant) and scan movement pattern (L = linear, Z = zig-zag, C = combined). Trueness was assessed by evaluating linear differences in the X, Y, and Z axes and angular deviations (α axial, α coronal, α total) compared to a reference dataset. Statistical differences were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests (p<0.017). Precision was analyzed by the standard deviation of linear and angular aberrations (ISO 5725-1) (p < 0.05).
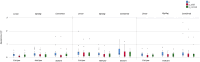
Results: Strategy FL showed significantly higher trueness and precision than FZ for VE (p = 0.009), VE(y) (p = 0.010), αoverall (p = 0.004), and αaxial (p = 0.002). Strategy FC demonstrated significantly better trueness than FZ for VE (p = 0.007), αoverall (p = 0.010), and αcoronal (p = 0.013). For scan segmentation, FL showed better trueness for VE(y) (p = 0.001) and αaxial (p < 0.001) than HL. Strategy HL showed better trueness for VE(z) than for FL and SL (p = 0.001, p = 0.002). The scanning patterns FL, FC, and HL exhibited the best performance for trueness and precision.
Conclusions: Scanning motion and segmentation have a significant impact on the trueness and precision of full-arch scans.
Clinical relevance: The scanning strategy is decisive in enhancing the clinical workflow and the accuracy of full-arch scans.
Keywords: Accuracy; Full-arch digitization; Intraoral scanner; Scanning strategies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Implant Scan Body type, Intraoral scanner and Scan Strategy on the accuracy and scanning time of a maxillary complete arch implant scans: an in vitro study.J Dent. 2025 Aug;159:105782. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2025.105782. Epub 2025 Apr 25. J Dent. 2025. PMID: 40288482
-
Scan accuracy and time efficiency of different implant-supported fixed partial denture situations depending on the intraoral scanner and scanned area: An in vitro study.J Prosthet Dent. 2024 Jun;131(6):1198-1207. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2023.01.029. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Prosthet Dent. 2024. PMID: 36868987
-
Evaluation of the accuracy of digital impressions with different scanning strategies: An in vitro study.J Dent. 2024 Dec;151:105433. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2024.105433. Epub 2024 Oct 28. J Dent. 2024. PMID: 39490607
-
Accuracy of full-arch digitalization for partially edentulous jaws - a laboratory study on basis of coordinate-based data analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Apr;26(4):3651-3662. doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-04335-3. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Clin Oral Investig. 2022. PMID: 34981252 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of scanning pattern on accuracy, time, and number of photograms of complete-arch implant scans: A clinical study.J Dent. 2024 Nov;150:105310. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2024.105310. Epub 2024 Aug 15. J Dent. 2024. PMID: 39153542
References
-
- Güth JF, Runkel C, Beuer F, Stimmelmayr M, Edelhoff D, Keul C (2017) Accuracy of five intraoral scanners compared to indirect digitalization. Clin Oral Investig 21:1445–1455 - PubMed
-
- Kühne C, Lohbauer U, Raith S, Reich S (2021) Measurement of tooth wear by means of digital impressions: an in-vitro evaluation of three intraoral scanning systems. Appl Sci 11:5161
-
- Suese K (2020) Progress in digital dentistry: the practical use of intraoral scanners. Dent Mater J 39:717–722 - PubMed
-
- Schweiger J, Kieschnick A (2020) CAD/CAM in digital dentistry. teamwork media GmbH
-
- Rehmann P, Sichwardt V, Wöstmann B (2017) Intraoral scanning systems: need for maintenance. Int J Comput Dent 20:367–373 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous