Robotic-assisted costectomy using a Gigli saw for fibrous dysplasia
- PMID: 39865275
- PMCID: PMC11771099
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-025-03340-x
Robotic-assisted costectomy using a Gigli saw for fibrous dysplasia
Abstract
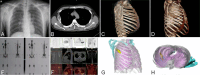
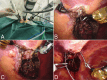
Background: Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is the most common benign tumor of the ribs, with surgical resection being the preferred treatment modality for rib FD, leading to enhanced quality of life and favorable outcomes. The complexity of surgical intervention varies depending on the location of costal FD, presenting challenges for both open surgical and thoracoscopic approaches. In this study, we present a novel technique for three-port robotic-assisted costectomy utilizing a Gigli saw, detailing our initial findings and outcomes.
Methods: We reviewed five patients with benign rib tumors who underwent three-port robotic-assisted rib resection using a Gigli saw between May 2021 and December 2022. Data on patient characteristics, relevant short-term surgical outcomes and clinical long-term treatment effects were collected.
Results: The surgery was successful in all five patients without any need for an additional port and emergency conversion to open surgery. Median operative time was 76.8 min (range, 73-116 min), and the median intraoperative blood loss volumes was 75 ml (range, 40- 105 mL). On average, chest tubes were removed 1.2 days postoperatively (range, 1-2 days), with a mean drainage volume of 93 ml on postoperative day 1 (range, 70-135 ml). Patients were discharged between the 2nd and 4th postoperative day. During 1-year follow-up period, no recurrence was observed in either patient.
Conclusions: The utilization of a three-port robotic-assisted costectomy in conjunction with a Gigli saw represents a viable, secure, and efficient approach for treating isolated benign rib lesions. Our aim is to provide clinical guidance on this technique and promote its broader application.
Keywords: Fibrous dysplasia; Gigli saw; Rib resection; Robot-assisted costectomy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional ethical committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. And all experimental protocols in the manuscript were approved by Soochow University. The ethics committee waived the requirement for informed consent due to the retrospective nature of the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rib resection using a Gigli saw under thoracoscopic guidance.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2019 Jan;14(1):126-132. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2018.77266. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2019. PMID: 30766639 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic-assisted wire saw resection of high-position rib tumors: a single-center experience.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Oct 31;15(10):5585-5592. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-983. Epub 2023 Oct 11. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37969296 Free PMC article.
-
Single-port thoracoscopic rib resection: a case report.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014 Mar 15;9:49. doi: 10.1186/1749-8090-9-49. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014. PMID: 24628945 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic outlet syndrome: a retrospective analysis of robotic assisted first rib resections.J Robot Surg. 2023 Jun;17(3):891-896. doi: 10.1007/s11701-022-01486-7. Epub 2022 Nov 3. J Robot Surg. 2023. PMID: 36327061 Review.
-
Robotic-Assisted First Rib Resection: Our Experience and Review of the Literature.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Winter;32(4):1115-1120. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2020.04.016. Epub 2020 May 21. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32446920 Review.
References
-
- Incarbone M, Pastorino U. Surgical treatment of chest wall tumors. World J Surg. 2001;25(2):218–30. - PubMed
-
- Anderson BO, Burt ME. Chest wall neoplasms and their management. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1774–81. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick KA, Taljanovic MS, Speer DP, Graham AR, Jacobson JA, Barnes GR, et al. Imaging findings of fibrous dysplasia with histopathologic and intraoperative correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182(6):1389–98. - PubMed
-
- Kransdorf MJ, Moser RP Jr., Gilkey FW. Fibrous dysplasia. Radiographics 1990;10(3):519–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

