Modeling the determinants of cigarette consumption in Iranian households with children under 5 years of age using the Income and Expenditure Survey 2021
- PMID: 39865296
- PMCID: PMC11765938
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-024-01496-x
Modeling the determinants of cigarette consumption in Iranian households with children under 5 years of age using the Income and Expenditure Survey 2021
Abstract
Background: Cigarette smoking remains a significant public health concern, with detrimental effects on both smokers and those exposed to secondhand smoke. This study investigates the factors influencing smoking behaviors in Iranian households, focusing on households with children under five years old.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of 8751 Iranian households using data from the Iranian Household Income and Expenditure Survey (HIES) collected by the Statistical Center of Iran (SCI) in 2021. A variety of count regression models were examined, including Poisson (P), Negative Binomial (NB), Generalized Poisson (GP) and their zero-inflated counterparts. The best fitting model was selected based on goodness-of-fit indices.
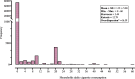
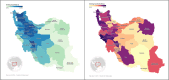
Results: Approximately 87% of households were non-smokers, with a mean daily cigarette consumption of 14.29 (SD = 8.64) among smokers. The three-level Zero-Inflated Generalized Poisson (TL-ZIGP) model was considered a suitable model for the interpretation of the data. Key predictors of smoking included older age, male gender, lower education, higher income, and larger homes. Homeownership was negatively associated with smoking. Considerable geographic variation in smoking prevalence was observed.
Conclusions: Socioeconomic and demographic factors, including lifestyle and geographic regions, are associated with smoking behavior among Iranian households. A three-level ZIGP regression model is appropriate for analyzing these complex relationships. This study reveals different patterns of smoking prevalence in different population subgroups and emphasizes the need for targeted interventions to effectively reduce smoking rates.
Keywords: Count regression models; Iranian households; Smoking behavior; Zero-inflated models.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ahvaz University of Medical Sciences (approval number IR.AJUMS.REC.1402.067). All procedures conform to the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees for human experimentation and the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975 as amended in 2008. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling the determinants of smoking behavior among young adults in Khuzestan province: a two-level count regression approach.Front Public Health. 2024 Nov 28;12:1449193. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1449193. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39703479 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette Smoking and Its Financial Burden among Iranian Households: Evidence from Household Income and Expenditures Survey.J Res Health Sci. 2020 Oct 13;20(4):e00494. doi: 10.34172/jrhs.2020.28. J Res Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 33424003 Free PMC article.
-
Models for analyzing zero-inflated and overdispersed count data: an application to cigarette and marijuana use.Nicotine Tob Res. 2018 Apr 18;22(8):1390-8. doi: 10.1093/ntr/nty072. Online ahead of print. Nicotine Tob Res. 2018. PMID: 29912423 Free PMC article.
-
Socioeconomic inequality in tobacco expenditure in Iran: a cross-sectional analysis at national and subnational levels.BMC Public Health. 2020 Jun 29;20(1):1031. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09144-z. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32600457 Free PMC article.
-
Current cigarette smoking among Iranian elders; what are the prevalence, inequality and socioeconomic determinants? An analysis on Iranian Rural and Urban Income-Expenditure Survey 2017.J Addict Dis. 2020 Jul-Sep;38(3):257-262. doi: 10.1080/10550887.2020.1747932. Epub 2020 Apr 15. J Addict Dis. 2020. PMID: 32293235
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

