Lifesaving surgical approaches for severe penetrating knife injury to the neck
- PMID: 39865304
- PMCID: PMC11771049
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-03233-5
Lifesaving surgical approaches for severe penetrating knife injury to the neck
Abstract
Background: Penetrating neck injuries are rare and require urgent surgical intervention to prevent life-threatening complications. This report highlights a unique case involving complex surgical repair of tracheal, esophageal, and vascular injuries following a homicidal assault, emphasizing the challenges and techniques used in managing such severe trauma.
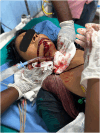
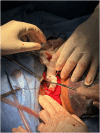
Case presentation: A 45-year-old female presented with a severe penetrating neck injury after an alleged homicidal assault with a knife. The patient was in hypovolemic shock and required immediate resuscitation. Endotracheal intubation was performed through the transected tracheal segment, followed by surgical exploration in the operating room. Findings included partial transection of the carotid sheath, complete transection of the trachea, and oesophagus. Surgical repair involved using lateral polypropylene 5-O sutures for the carotid sheath, end-to-end oesophageal repair with absorbable 3 - 0 polygalactin sutures. As tracheal repair was not possible posterior wall was approximated with 3 - 0 polypropylene and size 7 tracheostomy tube was inserted and secured. The patient was managed post-operatively in the ICU and was discharged in stable condition on the 25th day adviced regular follow-up. This case underscores the importance of prompt airway management and surgical intervention in penetrating neck injuries. The meticulous repair of all injured structures and diligent post-operative care are crucial to a successful outcome. This report contributes to the limited literature on managing complex penetrating stab injuries to the neck and highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in such cases.
Keywords: Carotid sheath; Hypovolemic shock; Oesophageal repair; Penetrating neck wounds injury; Tracheal transection; Tracheostomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethics approval was obtained from the ABC Hospital Ethics Committee (Ref: 2024-CTI-56). Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for participation in this case study. Consent for publication: Written informed consent for publication of this case report and any accompanying images was obtained from the patient. A copy of the consent form is available for review by the Editor of this journal. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Rare Self-Inflicted Stabbing to the Neck Injuring the Distal Trachea and Proximal Esophagus.Am Surg. 2023 Aug;89(8):3568-3569. doi: 10.1177/00031348231162703. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Am Surg. 2023. PMID: 36913718
-
Management of penetrating laryngotracheal injuries.Head Neck. 1995 Nov-Dec;17(6):494-502. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880170607. Head Neck. 1995. PMID: 8847208
-
Modern management of penetrating tracheal injuries.Am Surg. 2013 Feb;79(2):188-93. Am Surg. 2013. PMID: 23336659
-
[Penetrating injuries of the neck: review of 16 operated cases].Ann Ital Chir. 2003 Mar-Apr;74(2):141-8. Ann Ital Chir. 2003. PMID: 14577108 Review. Italian.
-
[Management of traumatic tracheal injuries: presentation of a rare case and review of the literature].Laryngorhinootologie. 2008 Apr;87(4):270-3. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-995403. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Laryngorhinootologie. 2008. PMID: 18200458 Review. German.
References
-
- Aich M, Alam AK, Talukder DC, Sarder MR, Fakir AY, Hossain M. Penetrating neck wounds injury: review of 67 cases. Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;17(1):5–13.
-
- Lama MS. Management of the homicidal penetrating neck wounds: an open airway injury. J Anesth Clin Care. 2019;6(1):42.
-
- Yadav A, Raheel MS, Kumar RL, Sharma SK, Kanwar H. Cut-throat wounds: suicidal and homicidal-two case reports and review of literature. Med Sci Law. 2016;56(1):53–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

