Modeling the response to interleukin-21 to inform natural killer cell immunotherapy
- PMID: 39865344
- PMCID: PMC11792776
- DOI: 10.1111/imcb.12848
Modeling the response to interleukin-21 to inform natural killer cell immunotherapy
Erratum in
-
Modeling the response to interleukin-21 to inform natural killer cell immunotherapy.Immunol Cell Biol. 2025 Sep;103(8):820. doi: 10.1111/imcb.70055. Epub 2025 Aug 15. Immunol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40814796 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
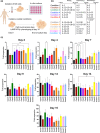
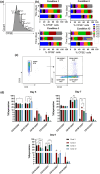
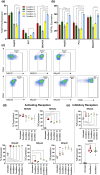
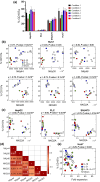
Natural killer (NK) cells are emerging agents for cancer therapy. Several different cytokines are used to generate NK cells for adoptive immunotherapy including interleukin (IL)-2, IL-12, IL-15 and IL-18 in solution, and membrane-bound IL-21. These cytokines drive NK cell activation through the integration of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathways, which overlap and synergize, making it challenging to predict optimal cytokine combinations for both proliferation and cytotoxicity. We integrated functional assays for NK cells cultured in a variety of cytokine combinations with mathematical modeling using feature selection and mechanistic regression models. Our regression model successfully predicts NK cell proliferation for different cytokine combinations and indicates synergy of activated STATs and NF-κB transcription factors between priming and post-priming phases. The use of IL-21 in solution in the priming of NK cell culture resulted in an improved NK cell proliferation, without compromising cytotoxicity potential or interferon gamma secretion against hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Our work provides an integrative framework for interrogating NK cell proliferation and activation for cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: NK cells; STAT; cytokines; linear regression; predictive model; proliferation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Immunology & Cell Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of the Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Becknell B, Caligiuri MA. Interleukin‐2, Interleukin‐15, and their roles in human natural killer cells. Adv Immunol 2005; 86: 209–239. - PubMed
-
- Klingemann HG, Martinson J. Ex vivo expansion of natural killer cells for clinical applications. Cytotherapy 2004; 6: 15–22. - PubMed
-
- Lee DA. Cellular therapy: adoptive immunotherapy with expanded natural killer cells. Immunol Rev 2019; 290: 85–99. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

