Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Imaging: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39865461
- PMCID: PMC11866320
- DOI: 10.1002/ueg2.12723
Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Imaging: A Systematic Review
Abstract
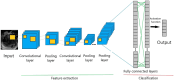
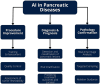
The rising incidence of pancreatic diseases, including acute and chronic pancreatitis and various pancreatic neoplasms, poses a significant global health challenge. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) for example, has a high mortality rate due to late-stage diagnosis and its inaccessible location. Advances in imaging technologies, though improving diagnostic capabilities, still necessitate biopsy confirmation. Artificial intelligence, particularly machine learning and deep learning, has emerged as a revolutionary force in healthcare, enhancing diagnostic precision and personalizing treatment. This narrative review explores Artificial intelligence's role in pancreatic imaging, its technological advancements, clinical applications, and associated challenges. Following the PRISMA-DTA guidelines, a comprehensive search of databases including PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane Library was conducted, focusing on Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and radiomics in pancreatic imaging. Articles involving human subjects, written in English, and published up to March 31, 2024, were included. The review process involved title and abstract screening, followed by full-text review and refinement based on relevance and novelty. Recent Artificial intelligence advancements have shown promise in detecting and diagnosing pancreatic diseases. Deep learning techniques, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have been effective in detecting and segmenting pancreatic tissues as well as differentiating between benign and malignant lesions. Deep learning algorithms have also been used to predict survival time, recurrence risk, and therapy response in pancreatic cancer patients. Radiomics approaches, extracting quantitative features from imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, and endoscopic ultrasound, have enhanced the accuracy of these deep learning models. Despite the potential of Artificial intelligence in pancreatic imaging, challenges such as legal and ethical considerations, algorithm transparency, and data security remain. This review underscores the transformative potential of Artificial intelligence in enhancing the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic diseases, ultimately aiming to improve patient outcomes and survival rates.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; endoscopic ultrasound; machine learning; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
© 2024 The Author(s). United European Gastroenterology Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of United European Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hegyi P., Párniczky A., Lerch M. M., et al., “Working Group for the International (IAP – APA – JPS – EPC) Consensus Guidelines for Chronic Pancreatitis. International Consensus Guidelines for Risk Factors in Chronic Pancreatitis. Recommendations From the Working Group for the International Consensus Guidelines for Chronic Pancreatitis in Collaboration With the International Association of Pancreatology, the American Pancreatic Association, the Japan Pancreas Society, and European Pancreatic Club,” Pancreatology 20, no. 4 (June 2020): 579–585, 10.1016/j.pan.2020.03.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jiang W., Du Y., Xiang C., Li X., and Zhou W., “Age‐Period‐Cohort Analysis of Pancreatitis Epidemiological Trends From 1990 to 2019 and Forecasts for 2044: A Systematic Analysis From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019,” Frontiers in Public Health 11 (June 2023): 1118888, 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1118888. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

