Early achievement of hemostasis defined by transfusion velocity: A possible mechanism for whole blood survival benefit
- PMID: 39865522
- PMCID: PMC11902607
- DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004507
Early achievement of hemostasis defined by transfusion velocity: A possible mechanism for whole blood survival benefit
Abstract
Introduction: Whole blood resuscitation is associated with survival benefits in observational cohort studies. The mechanisms responsible for outcome benefits have not been adequately determined. We sought to characterize the achievement of hemostasis across patients receiving early whole blood versus component resuscitation. We hypothesized that achieving hemostasis would be associated with outcome benefits and patients receiving whole blood would be more likely to achieve hemostasis.
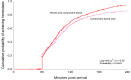
Methods: We performed a post hoc retrospective secondary analysis of data from a recent prospective observational cohort study comparing early whole blood and component resuscitation in patients at risk of hemorrhagic shock. Achievement of hemostasis was defined by receiving a single unit of blood or less, including whole blood or red cells, in any 60-minute period, over the first 4 hours from the time of arrival. Time-to-event analysis with log-rank comparison and regression modeling were used to determine the independent benefits of achieving hemostasis and whether achieving hemostasis was associated with whole blood resuscitation.
Results: For the current analysis, 1,047 patients met the inclusion criteria for the study. When we compared patients who achieved hemostasis versus those who did not, achievement of hemostasis had significantly more hemostatic coagulation parameters, had lower transfusion requirements, and was independently associated with 4-hour, 24-hour and 28-day survival. Whole blood patients were significantly more likely to achieve hemostasis (88.9% vs. 81.1%, p < 0.001). Whole blood patients achieved hemostasis earlier (log-rank χ 2 = 8.2, p < 0.01) and were independently associated with over twofold greater odds of achieving hemostasis (odds ratio, 2.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.6-3.7; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Achievement of hemostasis is associated with significant outcome benefits. Early whole blood resuscitation is associated with a greater independent odds of achieving hemostasis and at an earlier time point. Reaching a nadir transfusion rate early following injury represents a possible mechanism of whole blood resuscitation and its attributable outcome benefits.
Level of evidence: Therapeutic/Care Management; Level III.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

