Content Analysis of Food and Beverage Advertisements on TV, Radio, and Billboards in Iran
- PMID: 39865613
- PMCID: PMC11770774
- DOI: 10.1177/00469580251314775
Content Analysis of Food and Beverage Advertisements on TV, Radio, and Billboards in Iran
Abstract
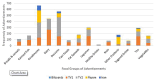
Food advertising may influence food preferences and consumption. Due to these advertisements' role in health, the present study has updated the data available on television and radio food advertisements in Iran until 2020. Meanwhile, food advertisements on billboards have been analyzed for the first time. All programs broadcast on two TV and radio channels were downloaded and saved 24 h daily for one week (November 10-16th, 2020). Also, on November 15th billboards located on the busy highways of Tehran were photographed. Validated protocols analyzed the advertisements. A total of 6026 advertisements were analyzed, including 4287 on TV, 1545 on radio, and 194 on billboards. The total duration of TV and radio advertising was 48.6 h. Food products were the most displayed advertisements on TV, radio, and billboards (33.6%). Overall, "condiments" and "desserts" were the most frequently advertised food products among all the studied media (20% and 17%, respectively). The most common advertising appeal included "High quality" on TV and billboards and "Stimulation of profiteering and profit-seeking" on the radio. Advertising violation based on Iran's regulations, Nutrient profile model for the marketing of food and non-alcoholic beverages to children in the WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region, and International Network for Food and Obesity / Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs) Research Monitoring and Action Support (INFORMAS) was reported to be 13%, 74%, and 51%, respectively. Food products ranked the highest among all the advertisements. A clear violation of domestic and international advertising regulations was observed which given the high share of food advertising in the studied media, could endanger public health. This study supports the need for stricter regulations and adherence to international standards to improve nutritional status.
Keywords: advertisements; content analysis; food and beverages; mass media; non-communicable diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutritional quality of foods and non-alcoholic beverages advertised on Mexican television according to three nutrient profile models.BMC Public Health. 2016 Aug 5;16:733. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3298-0. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27495000 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional quality of foods and non-alcoholic beverages advertised on Brazilian free-to-air television: a cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2020 Mar 24;20(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08527-6. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32209067 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of alcohol and alcohol-flavoured non-alcoholic beverage advertisements over Japanese free-to-air television networks.BMC Public Health. 2022 Oct 6;22(1):1864. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14276-5. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36203148 Free PMC article.
-
Unhealthy food and non-alcoholic beverage advertising on children's, youth and family free-to-air and digital television programmes in Thailand.BMC Public Health. 2018 Jun 15;18(1):737. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5675-3. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29902986 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Opportunities for Change in Food Marketing to Children and Youth: Workshop Summary.Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2013 May 14. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2013 May 14. PMID: 24872975 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). GBD Results Tools. 2023. Accessed January, 15, 2023. http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool
-
- Ebrahim S. Chronic Diseases and Calls to Action. Oxford University Press; 2008: 225-230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources