The future of siRNA-mediated approaches to treat von Willebrand disease
- PMID: 39865861
- PMCID: PMC11854048
- DOI: 10.1080/17474086.2025.2459259
The future of siRNA-mediated approaches to treat von Willebrand disease
Abstract
Introduction: The clinical management of the inherited bleeding disorder von Willebrand disease (VWD) focuses on normalizing circulating levels of von Willebrand factor (VWF) and factor VIII (FVIII) to prevent or control bleeding events. The heterogeneous nature of VWD, however, complicates effective disease management and development of universal treatment guidelines.
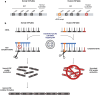
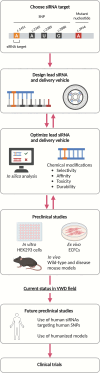
Areas covered: The current treatment modalities of VWD and their limitations are described and why this prompts the development of new treatment approaches. In particular, RNA-based therapeutics have gained significant interest because of their ability to reversibly alter gene expression with long-term efficacy. In the field of VWD, small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs) have been explored through various strategies to improve disease phenotypes. These different approaches are discussed as well as their potential impact on reshaping the future therapeutic landscape.
Expert opinion: Current treatments for VWD often require frequent intravenous administration of VWF concentrates or desmopressin, with only short-term benefits. Moreover, remaining circulating mutant VWF can cause detrimental effects. Allele-selective siRNA-based therapies could provide more reliable and long-term disease correction by specifically targeting mutant VWF. This approach could be applied to a large part of the population aligning with the growing emphasis on personalized treatment and patient-centered care in VWD management.
Keywords: RNA therapy; siRNA; treatment; von Willebrand disease; von Willebrand factor.
Conflict of interest statement
JCJ Eikenboom has received research funding from CSL Behring with all funds to the institution. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
