Predictive value of the systemic immune inflammation index in recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation
- PMID: 39866209
- PMCID: PMC11755125
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i1.102981
Predictive value of the systemic immune inflammation index in recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation
Abstract
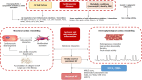
The recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients after successful radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) appears to be an unresolved clinical issue and needs to be clearly elucidated. There are many factors associated with AF recurrence, such as duration of AF, male sex, concomitant heart failure, hemodynamic parameters, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, hyperthyroidism, smoking and obesity. However, the inflammatory changes are strongly associated with electrical and structural cardiac remodeling, cardiac damage, myocardial fibrotic changes, microvascular dysfunction and altered reparative response. In this context, biomarkers reflecting the different stages of AF pathogenesis deserve thorough investigation. The authors of the retrospective study revealed that one-year recurrence rate of non-valvular AF in the high systemic immune inflammation (SII) index group was significantly increased compared to that of the low SII index group and provided additional predictive value to the APPLE. Furthermore, the authors suggest that this biomarker may help physicians to optimize the selection of AF patients and to develop a personalized treatment approach. In conclusion, the SII index may serve as a valuable indicator of recurrent AF in patients after RFCA and may be a biomarker with plausible predictive value for poor clinical outcomes.
Keywords: APPLE score; Biomarkers; Prediction; Radiofrequency catheter ablation; Recurrent atrial fibrillation; Systemic immune inflammation index.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The author declares no conflict of interest in publishing the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of a new inflammation predictor in predicting recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation.World J Cardiol. 2024 Dec 26;16(12):740-750. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i12.740. World J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39734822 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the systemic immune-inflammation index and outcomes among atrial fibrillation patients with diabetes undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation.Clin Cardiol. 2023 Nov;46(11):1426-1433. doi: 10.1002/clc.24116. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Clin Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37503809 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating inflammatory status to predict atrial fibrillation recurrence following ablation: The role of systemic immune-inflammation index.World J Cardiol. 2025 Mar 26;17(3):103074. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.103074. World J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40161571 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effects of Weight Loss and Catheter Ablation: Can microRNAs Serve as Predictive Biomarkers for the Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 25;25(9):4689. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094689. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width is a Biomarker of Red Cell Dysfunction Associated with High Systemic Inflammation and a Prognostic Marker in Heart Failure and Cardiovascular Disease: A Potential Predictor of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2024 Sep;31(5):437-449. doi: 10.1007/s40292-024-00662-0. Epub 2024 Jul 20. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2024. PMID: 39031283 Review.
References
-
- Lippi G, Sanchis-Gomar F, Cervellin G. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: An increasing epidemic and public health challenge. Int J Stroke. 2021;16:217–221. - PubMed
-
- Healey JS, Oldgren J, Ezekowitz M, Zhu J, Pais P, Wang J, Commerford P, Jansky P, Avezum A, Sigamani A, Damasceno A, Reilly P, Grinvalds A, Nakamya J, Aje A, Almahmeed W, Moriarty A, Wallentin L, Yusuf S, Connolly SJ RE-LY Atrial Fibrillation Registry and Cohort Study Investigators. Occurrence of death and stroke in patients in 47 countries 1 year after presenting with atrial fibrillation: a cohort study. Lancet. 2016;388:1161–1169. - PubMed
-
- Parameswaran R, Al-Kaisey AM, Kalman JM. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: current indications and evolving technologies. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18:210–225. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

