Melanoma cell line-derived exosomal miR-424-5p: a key promoter of angiogenesis through LATS2 interaction
- PMID: 39866229
- PMCID: PMC11753990
- DOI: 10.32604/or.2024.050878
Melanoma cell line-derived exosomal miR-424-5p: a key promoter of angiogenesis through LATS2 interaction
Abstract
Objectives: Melanoma is a highly aggressive and metastatic form of cancer, and the role of exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) in its progression remains largely unexplored. This study aimed to investigate the effects of melanoma cell-derived exosomal miR-424-5p on angiogenesis and its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Exosomes were isolated from melanoma cell lines A375 and A2058, and their effects on the proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were examined. The interaction between miR-424-5p and its target gene, large tumor suppressor kinase 2 (LATS2), was analyzed using luciferase reporter assays and functional experiments. In vivo, tumor growth and angiogenesis were studied in a xenograft model using nude mice.
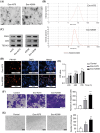
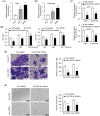
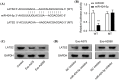
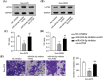
Results: Melanoma cell-derived exosomes could be internalized by HUVECs, which promoted proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. miR-424-5p was highly expressed in melanoma cells and their exosomes, and its inhibition in exosomes suppressed HUVEC proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. LATS2 was identified as a direct target of miR-424-5p, and its silencing reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-424-5p inhibition on HUVEC functions. In vivo, exosomes derived from miR-424-5p-inhibited melanoma cells suppressed tumor growth and angiogenesis in xenograft models.
Conclusions: Melanoma cell-derived exosomal miR-424-5p promotes angiogenesis by targeting LATS2, contributing to melanoma progression. Targeting the exosomal miR-424-5p/LATS2 axis could be a potential therapeutic strategy for melanoma.
Keywords: Cancer progression; Cell proliferation; Exosomal miR-424-5p; Large tumor suppressor kinase 2 (LATS2); Therapeutic targets.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
miR-493-5p Silenced by DNA Methylation Promotes Angiogenesis via Exosomes and VEGF-A-Mediated Intracellular Cross-Talk Between ESCC Cells and HUVECs.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jul 16;19:7165-7183. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S464403. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39050873 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from endometrial stromal cells promotes angiogenesis by targeting TIMP3 in ovarian endometrial cysts.J Mol Med (Berl). 2024 Nov;102(11):1327-1342. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02483-z. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2024. PMID: 39227403
-
Pancreatic cancer cell-derived exosomal microRNA-27a promotes angiogenesis of human microvascular endothelial cells in pancreatic cancer via BTG2.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(1):588-604. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14766. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31724333 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CAF derived exosomal microRNAs in the tumour microenvironment of melanoma.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188456. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188456. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33153973 Review.
-
Dual role of miR-155 and exosomal miR-155 in tumor angiogenesis: implications for cancer progression and therapy.Eur J Med Res. 2025 May 19;30(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02618-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40383762 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centeno PP, Pavet V, Marais R. The journey from melanocytes to melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023;23(6):372–90; - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49; - PubMed
-
- Luke JJ, Flaherty KT, Ribas A, Long GV. Targeted agents and immunotherapies: optimizing outcomes in melanoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14(8):463–82; - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
