Key personal insights and changing needs of osteoarthritis patients: an international quantitative survey analysis
- PMID: 39866304
- PMCID: PMC11758104
- DOI: 10.5114/reum/195324
Key personal insights and changing needs of osteoarthritis patients: an international quantitative survey analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA) presents significant challenges, imposing limitations on patients' daily activities. Factors such as restricted mobility, sedentary lifestyles, social isolation, and weight gain can exacerbate the difficulties faced by these individuals. Our study aimed to identify the needs and personal challenges faced by individuals with OA, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Material and methods: The research included a quantitative survey and a workshop involving a Scientific Leader Team. The quantitative survey was conducted among 400 patients in Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, and Kazakhstan. All enrolled participants had experienced chronic musculoskeletal pain due to OA for at least three years and had received treatment with topical or oral medications. The cross-country workshop, conducted via Zoom, brought together prominent rheumatologists to discuss the survey results and explore patient support opportunities with healthcare providers.
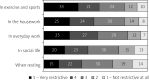
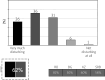
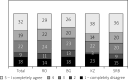
Results: Over 60% of respondents reported that poor locomotor function adversely affected their daily activities. More than 50% stated that they had delayed treatment due to concerns about potential side effects, while over half expressed a desire for rapid pain relief. Approximately 30% of patients reported an increase in musculoskeletal complaints following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. The proportion of online consultations rose significantly, increasing from 5% before the pandemic to 12% during it, before stabilizing at 9% in the post-pandemic period.
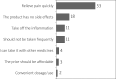
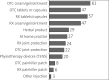
Conclusions: Patients with OA face considerable limitations in their daily lives, with a strong preference for immediate pain relief. Concerns about side effects lead many to postpone treatment. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory creams and prescription oral anti-inflammatory drugs are the most used therapies. The pandemic negatively affected OA symptoms. Furthermore, the use of online channels for OA patient care increased during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; NSAIDs; OA treatment; musculoskeletal pain; osteoarthritis.
Copyright: © 2024 Narodowy Instytut Geriatrii, Reumatologii i Rehabilitacji w Warszawie.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr András Bajkó and Dr Hajnalka Minda are employees of Gedeon Richter PLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Letter to the Editor: THE IMPACT OF THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC ON SCHIZOPHRENIA PATIENTS.Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2021 Fall;32(3):219-221. doi: 10.5080/u26175. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2021. PMID: 34637131 English, Turkish.
-
Intra-articular viscosupplementation with hylan g-f 20 to treat osteoarthritis of the knee: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(10):1-66. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074461 Free PMC article.
-
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment for Pain Management in Patients With Osteoarthritis: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Aug 26;15(8):e44168. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44168. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37753003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes to consultations and diagnosis of osteoarthritis in primary care during the COVID-19 pandemic.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023 Jun;31(6):829-838. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2023.02.075. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023. PMID: 36878380 Free PMC article.
-
Relative safety and efficacy of topical and oral NSAIDs in the treatment of osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 9;101(36):e30354. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030354. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36086745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valdes AM, Stocks J. Osteoarthritis and Ageing. Eur Med J 2018; 3: 116–123, DOI: 10.1186/s12891-020-03195-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
