Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanism of exogenous melatonin improves salt tolerance in eggplants
- PMID: 39866315
- PMCID: PMC11759302
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1523582
Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanism of exogenous melatonin improves salt tolerance in eggplants
Abstract
Introduction: Melatonin significantly enhances the tolerance of plants to biotic and abiotic stress, and plays an important role in plant resistance to salt stress. However, its role and molecular mechanisms in eggplant salt stress resistance have been rarely reported. In previous studies, we experimentally demonstrated that melatonin can enhance the salt stress resistance of eggplants.
Methods: In this study, we treated salt-stressed eggplant plants with melatonin and a control treatment with water, then conducted physiological and biochemical tests, transcriptomic and metabolomic sequencing, and RT-qPCR validation at different stages after treatment.
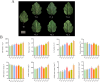
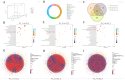
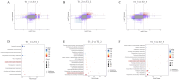
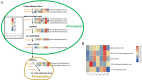
Results: The results showed that exogenous melatonin can alleviate the adverse effects of salt stress on plants by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes, reducing the content of reactive oxygen species in plants, and increasing the content of organic osmoprotectants. Transcriptomic and metabolomic data, as well as combined analysis, indicate that melatonin can activate the metabolic pathways of plant resistance to adverse stress. Compared to the control treatment with water, melatonin can activate the genes of the α-linolenic acid metabolism pathway and promote the accumulation of metabolites in this pathway, with significant effects observed 48 hours after treatment, and significantly activates the expression of genes such as SmePLA2, SmeLOXs and SmeOPR et al. and the accumulation of metabolites such as α-Linolenic acid, (9R,13R)-12-oxophytodienoic acid, 9(S)-HpOTrE and (+)-7-iso-Jasmonic acid. RT-qPCR validated the activating effect of melatonin on the candidate genes of the a-linolenic acid metabolism pathway.
Discussion: This study analyzed the molecular mechanism of melatonin in alleviating eggplant salt stress, providing a theoretical foundation for the application of melatonin in enhancing eggplant salt stress resistance in production.
Keywords: eggplant; melatonin; metabolomic; salt stress; transcriptomic; α-linolenic acid.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhang, Jiang, Ding, Wang, Wang, Yan and Jia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Melatonin-induced physiology and transcriptome changes in banana seedlings under salt stress conditions.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 6;13:938262. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.938262. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36147243 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the role of exogenous melatonin in mitigating alkaline stress in soybeans across different growth stages: a transcriptomic and metabolomic approach.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 8;24(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05101-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38720246 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative physiological, metabolomic, and transcriptomic analyses reveal mechanisms of improved abiotic stress resistance in bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L). Pers.] by exogenous melatonin.J Exp Bot. 2015 Feb;66(3):681-94. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru373. Epub 2014 Sep 15. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25225478 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Melatonin in Salt Stress Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 8;20(7):1735. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071735. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30965607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin: A Small Molecule but Important for Salt Stress Tolerance in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 7;20(3):709. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030709. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30736409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phenylpropanoids metabolism: recent insight into stress tolerance and plant development cues.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 26;16:1571825. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1571825. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40641862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cai S., Xu S., Zhang D., Fu Z., Zhang H., Zhu H. (2022). Phytoremediation of Secondary Salinity in Greenhouse Soil with Astragalus sinicus, Spinacea oleracea and Lolium perenne. Agriculture 12, 212. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12020212 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

