New horizons in the treatment of psoriasis: Modulation of gut microbiome
- PMID: 39866422
- PMCID: PMC11760288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41672
New horizons in the treatment of psoriasis: Modulation of gut microbiome
Abstract
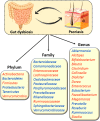
The last decennia have witnessed spectacular advances in our knowledge about the influence of the gut microbiome on the development of a wide swathe of diseases that extend beyond the digestive tract, including skin diseases like psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, acne vulgaris, rosacea, alopecia areata, and hidradenitis suppurativa. The novel concept of the gut-skin axis delves into how skin diseases and the microbiome interact through inflammatory mediators, metabolites, and the intestinal barrier. Elucidating the effects of the gut microbiome on skin health could provide new opportunities for developing innovative treatments for dermatological diseases. Psoriasis is a complex disease with multiple factors contributing to its development, such as diet, lifestyle, genetic predisposition, and the microbiome. This paper has a dual purpose. First, we outline the current knowledge on the unique gut microbiota patterns implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Second, and of equal importance, we briefly discuss the reciprocal impact of psoriasis treatment and gut microbiome. In addition, this review explores potential therapeutic targets based on microbial interventions, which hold promise for providing new treatment options for psoriasis.
Keywords: Dysbiosis; Microbiota; Probiotics; Psoriasis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2096995. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 35866234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting dysbiosis in psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa: the gut-skin axis and microbiome-directed therapy.Clin Dermatol. 2023 Sep-Oct;41(5):640-649. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2023.09.019. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Clin Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37816413 Review.
-
Gut-Skin Axis: Unravelling the Connection between the Gut Microbiome and Psoriasis.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 30;10(5):1037. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051037. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotics and gut microbiota modulation: implications for skin health and disease management.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Feb 23;207(3):68. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04267-6. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39988585 Review.
-
Gut-Skin Axis: Current Knowledge of the Interrelationship between Microbial Dysbiosis and Skin Conditions.Microorganisms. 2021 Feb 11;9(2):353. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020353. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33670115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges Psoriasis and Its Impact on Quality of Life: Challenges in Treatment and Management.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2025 May 1;15:175-183. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S519420. eCollection 2025. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2025. PMID: 40330837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kimmel G.W., Lebwohl M. In: Evidence-Based Psoriasis. Bhutani T., Liao W., Nakamura M., editors. Springer; Cham: 2018. Psoriasis: overview and diagnosis. (Updates in Clinical Dermatology). - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

