Optimization of the extraction methods and evaluation of the hypoglycemic effect of Adhatoda Zeylanica extracts on artificially induced diabetic mice
- PMID: 39866458
- PMCID: PMC11758211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41627
Optimization of the extraction methods and evaluation of the hypoglycemic effect of Adhatoda Zeylanica extracts on artificially induced diabetic mice
Abstract
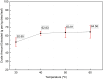
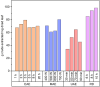
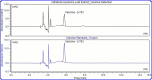
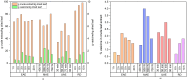
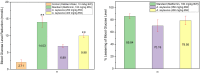
Synthetic antidiabetic drugs are often associated with various adverse side effects, including hypoglycemia, nausea, gastrointestinal disturbances, headaches, and even liver damage. In contrast, plant-derived natural antidiabetic bioactive compounds typically exhibit lower toxicity and fewer side effects and have been reported to aid effectively in diabetes management. These plant extracts regulate diabetes by restoring pancreatic function, enhancing insulin secretion, inhibiting intestinal glucose absorption, and facilitating insulin dependent metabolism. This study explored four extraction methods, including reflux distillation (RD), ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE), microwave assisted extraction (MAE), and enzyme assisted extraction (EAE) to optimize the yield of crude leaf extract and vasicine from Adhatoda zeylanica. RD produced the highest crude extract yield (98.29 g/kg of dried leaf), while MAE was the most effective for vasicine extraction, yielding 2.44 g vasicine per kg dried leaf. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with a diode array detector (DAD) was used to identify and quantify vasicine, a quinazoline alkaloid with known antidiabetic properties. The hypoglycemic effects of leaf extracts were evaluated in alloxan-induced diabetic mice, and the effect of A. zeylanica extract was compared to the extracts of Centella asiatica, Allamanda cathartica, and the standard drug metformin. At a dose of 400 mg/kg body weight (BW), methanolic leaf extracts of A. zeylanica, C. asiatica, and A. cathartica reduced blood glucose level by 78.95 %, 74.50 %, and 70.19 %, respectively, compared to the standard drug metformin, which reduced blood glucose levels by 85.84 %. A. zeylanica at 400 mg/kg BW dose and metformin demonstrated statistically similar and significant blood glucose level reduction (p < 0.001). Additionally, therapeutic doses of A. zeylanica leaf extract exhibited low cytotoxicity (cell survival rate >89 %), highlighting its potential as a safe and effective source of antidiabetic agent.
Keywords: Adhatoda zeylanica; Allamanda cathartica; Centella asiatica; Diabetes; Vasicine.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Green extraction optimization of triterpenoid glycoside-enriched extract from Centella asiatica (L.) Urban using response surface methodology (RSM).Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 11;11(1):22026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01602-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34764384 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of an HPLC-DAD method for Rapid quantification of vasicine in Adhatoda vasica leaves and commercial products.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 15;8(8):e10226. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10226. eCollection 2022 Aug. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36090217 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Potential of Extract Fraction of Quercus baloot Griff Seeds in Alloxan-induced Diabetic Mice.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(37):2978-2991. doi: 10.2174/0113816128319184240827070016. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39219120
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Comparative Studies on Different Extraction Methods of Centella asiatica and Extracts Bioactive Compounds Effects on Antimicrobial Activities.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Apr 17;10(4):457. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10040457. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kasali F., et al. Phytochemical constituents found in Physalis peruviana L. leaf extracts and their ability to inhibit alpha-glucosidase and scavenge DPPH free radicals in vitro. Trends Phytochem. Res. May 2022;6(1) doi: 10.30495/tpr.2022.1946170.1230. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

