The development and application of compound formulation of natural antioxidants in Idesia polycarpa maxim. Oil
- PMID: 39866486
- PMCID: PMC11759631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41648
The development and application of compound formulation of natural antioxidants in Idesia polycarpa maxim. Oil
Abstract
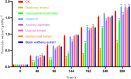
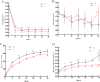
Idesia polycarpa Maxim. is valued for its high oil yield, which fruit has high oil content and good health effects. However, the large amount of unsaturated fatty acids in the oil is easily oxidized, and its storage intolerance has seriously restricted its marketing. In order to slow down the oxidation rate of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. oil, this study found that the most effective single antioxidant was rosemary extract through the screening of seven different natural antioxidants. The experiments were designed using the response surface method to compound three individual natural antioxidants with good anti-oxidative effects, namely rosemary extract, tea polyphenol palmitate, and ascorbic acid palmitate. A comprehensive model was established to determine the optimal anti-oxidative compound formulation, which was found to be 0.45 g/kg of rosemary extract +0.21 g/kg of tea polyphenol palmitate. The effectiveness of the best compounded natural antioxidants under simulated frying temperature (160 °C) was then examined. The results showed that the antioxidant capacity of the compound formulation was significantly increased, and the generation of secondary oxidation products was inhibited and the loss of unsaturated fatty acids was reduced. Therefore, the compound antioxidant-added Idesia polycarpa Maxim. oil not only showed good storage resistance, but also improved the safety of use under high temperature environment. The results of this study significantly improved the oxidative stability of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. oil, provided a theoretical basis for replacing synthetic antioxidants, promoted the industrial development of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. oil and expanded other applications.
Keywords: High temperature; Idesia polycarpa Maxim. oil; Natural antioxidants; Oil quality; Peroxide value.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu Z., Wang Q., Ruan X., Li Z., Xue J., Jiang H., Lu X. Analysis of oil rate and fatty acids content of Idesia polycarpa fruits from different geographical populations. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2010;46:176–180. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20100528. - DOI
-
- Wang H., Rana S., Li Z., Geng X., Wang Y., Cai Q., Li S., Sun J., Liu Z. Morphological and anatomical changes during floral bud development of the trioecious Idesia polycarpa Maxim. Rev. Bras. Bot. 2022;45:679–688. doi: 10.1007/S40415-022-00792-6/FIGURES/9. - DOI
-
- Jia R., Tang X., Dong N., Tang L., Chen F. Influence of different mature degrees on seeds germination and quality of fruit oil of Idesia polycarpa maxim. Var. vestita diels. Seed. 2014;33:38–41. doi: 10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.2014.09.070. - DOI
-
- Tian X., Wang L., Fang X., Du M. Effects of drying methods on physicochemical properties, fatty acid composition and trace nutrient contents of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. seed oil, China Oils Fats. 2020;45:8–11+55. doi: 10.12166/j.zgyz.1003-7969/2020.01.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources