Altered expression of miRNA profile in peripheral blood mononuclear cells following the third dose of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine
- PMID: 39866557
- PMCID: PMC11760199
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18856
Altered expression of miRNA profile in peripheral blood mononuclear cells following the third dose of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine
Abstract
COVID-19 vaccination is the most effective strategy for preventing severe disease and death. Inactivated vaccines are the most accessible type of COVID-19 vaccines in developing countries. Several studies, including work from our group, have demonstrated that the third dose (booster vaccination) of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine induces robust humoral and cellular immune responses. The present study aimed to examine miRNA expression profile in participants who received a homologous third dose of the CoronaVac vaccine. Samples of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected from healthcare volunteers both before and 1-2 weeks after the booster dose. miRNA microarray analysis in a discovery cohort of six volunteers identified 67 miRNAs with differential expression. Subsequently, the expression of six miRNAs related to immune responses was examined in a validation cohort of 31 participants via qRT-PCR. Our results validated the differential expression of miR-25-5p, miR-34c-3p, and miR-206 post-booster, with a significant correlation to the receptor binding domain (RBD)-specific antibody. Bioinformatic analysis suggested that miR-25-5p, miR-34c-3p, and miR-206 may target multiple pathways involved in immune regulation and inflammation. Therefore, our study highlights miR-25-5p, miR-34c-3p, and miR-206 in PBMCs as promising biomarkers for assessing the immune response induced by the booster dose of the CoronaVac vaccine.
Keywords: COVID-19; CoronaVac; Immune response; Inactivated vaccine; MicroRNA; Peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
© 2025 Qiu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
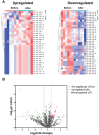



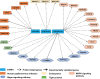
Similar articles
-
Immune responses and transcription landscape of adults with the third dose of homologous and heterologous booster vaccines of COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 12;15:1461419. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1461419. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39328415 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of different combinations involving a third booster dose of SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine, inactivated quadrivalent influenza vaccine, and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine in adults aged ≥60 years: a phase 4, randomized, open-label study.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 20;15:1437267. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437267. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39229259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of long-term anti-RBD SARS-CoV-2 antibody response following different vaccination schemes in Tunisia.Tunis Med. 2024 Aug 5;102(8):457-464. doi: 10.62438/tunismed.v102i8.4944. Tunis Med. 2024. PMID: 39129572 Free PMC article. English.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in health care workers.J Med Virol. 2022 Apr;94(4):1442-1449. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27458. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34783049 Free PMC article.
-
The immunogenicity and reactogenicity of four COVID-19 booster vaccinations against SARS-CoV-2 variants following CoronaVac or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 primary series.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2024 Sep;42(3):276-289. doi: 10.12932/AP-160123-1533. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37466962
References
-
- AbdelMassih A, Agha H, El-Saiedi S, El-Sisi A, El Shershaby M, Gaber H, Ismail HA, El-Husseiny N, Amin AR, ElBoraie A, Ayad A, Menshawey E, Sefein F, Osman II, Moursi M, Hanafy M, Abdelaziz MS, Arsanyous MB, Khaled-Ibn-El-Walid M, Tawfik MG, Habib M, Mansour ME, Ashraf M, Khattab MA, Alshehry N, Hafez N, ElDeeb NE, Ashraf N, Khalil N, AbdElSalam NI, Shebl N, Hafez NGA, Youssef NH, Bahnan O, Ismail P, Kelada P, Menshawey R, Saeed R, Husseiny RJ, Yasser R, Sharaf S, Adel V, Naeem Y, Nicola YNF, Kamel A, Hozaien R, Fouda R. The role of miRNAs in viral myocarditis, and its possible implication in induction of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines-induced myocarditis. Bulletin of the National Research Centre. 2022;46(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s42269-022-00955-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

