Protective effects of resveratrol on the expression of catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase genes in the ovary and their activity in the serum of rats exposed to lead acetate: An experimental study
- PMID: 39866587
- PMCID: PMC11757674
- DOI: 10.18502/ijrm.v22i11.17821
Protective effects of resveratrol on the expression of catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase genes in the ovary and their activity in the serum of rats exposed to lead acetate: An experimental study
Abstract
Background: Lead (Pb) could be toxic to the female reproductive system, and resveratrol (Res) may overcome this toxicity.
Objective: To investigate the Res impact on the catalase (Cat), glutathione peroxidase (Gpx), and superoxide dismutase (Sod) gene expression in the ovary and on the Cat and Gpx enzyme activity in the serum of rats exposed to lead acetate.
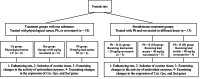
Materials and methods: In this experimental study, 33 female Wistar rats (8-10 wk, 180-200 gr) were divided into 6 groups: a control group (normal saline), a Res group (40 mg/kg), and a Pb group (lead acetate 30 mg/kg). 3 additional groups received lead acetate (30 mg/kg) with Res at 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg for 21 days. Gene expression of Cat, Gpx, and Sod was measured via qPCR, and serum Cat and Gpx activity was assessed using standard methods. Bioinformatics tools were used to evaluate Res effects on gene and protein function.
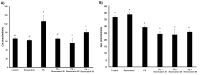
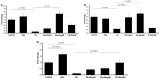
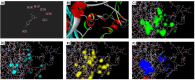
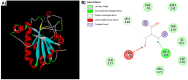
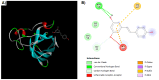
Results: Lead acetate significantly downregulates Cat, Gpx, and Sod gene expression, but Res significantly upregulates gene expression, especially at doses of 40 mg/kg for Cat, 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg for Gpx, and 80 mg/kg for Sod. Cat and Gpx enzyme activity increased and decreased in the lead acetate group, respectively. However, Res in all doses decreased only the Cat enzyme activity. Bioinformatics analysis indicates that Res can interact with the promoter regions and cavities of all 3 enzymes.
Conclusion: Pb can dysregulate the expression and activity of the studied enzymes. However, the impact of Res is influenced by the dose, with 40 mg/kg frequently being the most effective.
Keywords: In silico; Lead acetate; Ovary; Oxidative stress; Rat.; Resveratrol.
Copyright © 2024 Karimian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and NADPH oxidase in lead-induced hypertension.Kidney Int. 2003 Jan;63(1):186-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00711.x. Kidney Int. 2003. PMID: 12472782
-
Influence of iron on modulation of the antioxidant system in rat brains exposed to lead.Environ Toxicol. 2017 Mar;32(3):813-822. doi: 10.1002/tox.22281. Epub 2016 May 12. Environ Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27170105
-
Resveratrol improves sperm parameter and testicular apoptosis in cisplatin-treated rats: Effects on ERK1/2, JNK, and Akt pathways.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019 Jun;65(3):236-249. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2018.1541114. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019. PMID: 30507263
-
The Potency of Red Seaweed (Eucheuma cottonii) Extracts as Hepatoprotector on Lead Acetate-induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Jul-Sep;9(3):282-286. doi: 10.4103/pr.pr_69_16. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 28827971 Free PMC article.
-
Lead-induced oxidative damage in rats/mice: A meta-analysis.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020 Mar;58:126443. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.126443. Epub 2019 Dec 4. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31841831 Review.
References
-
- He Y, Wang L, Li X, Zhao H. The effects of chronic lead exposure on the ovaries of female juvenile Japanese quails (Coturnix japonica): Developmental delay, histopathological alterations, hormone release disruption and gene expression disorder. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;205:111338. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
