This is a preprint.
Does SARS-CoV-2 Infection Increase Risk of Neuropsychiatric and Related Conditions? Findings from Difference-in-Differences Analyses
- PMID: 39866876
- PMCID: PMC11760242
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5621095/v1
Does SARS-CoV-2 Infection Increase Risk of Neuropsychiatric and Related Conditions? Findings from Difference-in-Differences Analyses
Update in
-
Risk of neuropsychiatric and related conditions associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a difference-in-differences analysis.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 24;16(1):6829. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61961-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40707478 Free PMC article.
Abstract
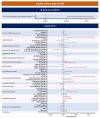
The COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with increased neuropsychiatric conditions in children and youths, with evidence suggesting that SARS-CoV-2 infection may contribute additional risks beyond pandemic stressors. This study aimed to assess the full spectrum of neuropsychiatric conditions in COVID-19 positive children (ages 5-12) and youths (ages 12-20) compared to a matched COVID-19 negative cohort, accounting for factors influencing infection risk. Using EHR data from 25 institutions in the RECOVER program, we conducted a retrospective analysis of 326,074 COVID-19 positive and 887,314 negative participants matched for risk factors and stratified by age. Neuropsychiatric outcomes were examined 28 to 179 days post-infection or negative test between March 2020 and December 2022. SARS-CoV-2 positivity was confirmed via PCR, serology, or antigen tests, while negativity required negative test results and no related diagnoses. Risk differences revealed higher frequencies of neuropsychiatric conditions in the COVID-19 positive cohort. Children faced increased risks for anxiety, OCD, ADHD, autism, and other conditions, while youths exhibited elevated risks for anxiety, suicidality, depression, and related symptoms. These findings highlight SARS-CoV-2 infection as a potential contributor to neuropsychiatric risks, emphasizing the importance of research into tailored treatments and preventive strategies for affected individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations Potential conflict of interest Dr. Jhaveri is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Seqirus, Dynavax, receives an editorial stipend from Elsevier and Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and royalties from Up To Date/Wolters Kluwer.
Figures


References
-
- Rosenthal E. et al. Impact of COVID-19 on Youth With ADHD: Predictors and Moderators of Response to Pandemic Restrictions on Daily Life. J Atten Disord 26, 1223–1234 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

