Neurotherapeutic impact of vanillic acid and ibudilast on the cuprizone model of multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 39866908
- PMCID: PMC11760597
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1503396
Neurotherapeutic impact of vanillic acid and ibudilast on the cuprizone model of multiple sclerosis
Abstract
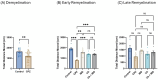
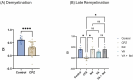
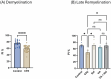
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects 2.8 million people worldwide. Although the cause is unknown, various risk factors might be involved. MS involves the immune system attacking the central nervous system's myelin sheath, leading to neuron damage. This study used a cuprizone (CPZ)-intoxicated mouse model to simulate MS's demyelination/remyelination process. It evaluated the molecular, histological, and behavioral effects of vanillic acid (VA), a natural phenolic acid, alone and with Ibudilast (IBD), a clinically tested MS medication. Mice were divided into a control group (regular chow) and a CPZ group (0.3% cuprizone chow for 5 consecutive weeks). During remyelination, the CPZ group was split into four groups: no therapy, 10 mg/kg of IBD, 30 mg/kg of VA, and combined, each treated for 4 weeks. Behavioral, biochemical, molecular, and histopathological tests occurred in the 5th week (demyelination), 7th (early remyelination), and 9th (late remyelination). Cognitive assessments were at weeks 5 and 9. VA enhanced motor, coordination, and cognitive impairments in CPZ-intoxicated mice and improved histopathological, molecular, and biochemical features during early remyelination. IBD improved behavioral abnormalities across all tests, but combined therapy showed no significant difference from single therapies. Further investigations are necessary to understand VA's mechanisms and potential as an MS treatment.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; cuprizone model; ibudilast; multiple sclerosis; vanillic acid.
Copyright © 2025 Alderbi, Alam, Alghamdi, Alsufiani, Abd El-Aziz, Omar and Al-Ghamdi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Alderbi R. M., Alshahrany G. A., Alyami K. A., Alsufiani H. M., Omar U. M., Al-Ghamdi M. A. (2022). Anti-inflammatory compounds ameliorate locomotion and anxiety behaviors in Cuprizone mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 59:103618. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.103618, PMID: - DOI
-
- Al-Otaibi K. M., Alghamdi B. S., Al-Ghamdi M. A., Mansouri R. A., Ashraf G. M., Omar U. M. (2022). Therapeutic effect of combination vitamin D3 and siponimod on remyelination and modulate microglia activation in cuprizone mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 16:1068736. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1068736, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

