Bioengineering strategies targeting angiogenesis: Innovative solutions for osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- PMID: 39866964
- PMCID: PMC11760140
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314241310541
Bioengineering strategies targeting angiogenesis: Innovative solutions for osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Abstract
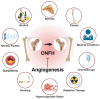
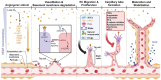
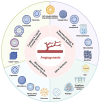
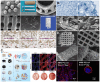
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) is a prevalent orthopedic disorder characterized primarily by compromised blood supply. This vascular deficit results in cell apoptosis, trabecular bone loss, and structural collapse of the femoral head at late stage, significantly impairing joint function. While MRI is a highly effective tool for diagnosing ONFH in its early stages, challenges remain due to the limited availability and high cost of MRI, as well as the absence of routine MRI screening in asymptomatic patients. . In addition, current therapeutic strategies predominantly only relieve symptoms while disease-modifying ONFH drugs are still under investigation/development. Considering that blood supply of the femoral head plays a key role in the pathology of ONFH, angiogenic therapies have been put forward as promising treatment options. Emerging bioengineering interventions targeting angiogenesis hold promising potential for ONFH treatment. In this review, we introduce the advances in research into the pathology of ONFH and summarize novel bioengineering interventions targeting angiogenesis. This review sheds light upon new directions for future research into ONFH.
Keywords: Osteonecrosis; angiogenesis; biomaterial scaffold; delivery system; femoral head.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of biomaterials in treating early osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Research progress and future perspectives.Acta Biomater. 2023 Jul 1;164:15-73. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37080444 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles from human urine-derived stem cells inhibit glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by transporting and releasing pro-angiogenic DMBT1 and anti-apoptotic TIMP1.Acta Biomater. 2020 Jul 15;111:208-220. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.020. Epub 2020 May 22. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32447063
-
Key pathway to prevent the collapse of femoral head in osteonecrosis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Aug;19(15):2766-74. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26241528
-
Analysis of the Potential Angiogenic Mechanisms of BuShenHuoXue Decoction against Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Orthop Surg. 2024 Mar;16(3):700-717. doi: 10.1111/os.13970. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 38296807 Free PMC article.
-
Review of various treatment options and potential therapies for osteonecrosis of the femoral head.J Orthop Translat. 2015 Oct 24;4:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2015.09.005. eCollection 2016 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2015. PMID: 30035066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Malizos KN, Karantanas AH, Varitimidis SE, et al.. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: etiology, imaging and treatment. Eur J Radiol 2007; 63(1): 16–28. - PubMed
-
- Mont MA, Cherian JJ, Sierra RJ, et al.. Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: where do we stand today? A ten-year update. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2015; 97(19): 1604–1627. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

