Biomimic models for in vitro glycemic index: Scope of sensor integration and artificial intelligence
- PMID: 39867218
- PMCID: PMC11764032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.102132
Biomimic models for in vitro glycemic index: Scope of sensor integration and artificial intelligence
Abstract
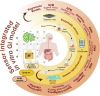
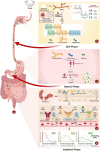
The accurate quantification of glycemic index (GI) remains crucial for diabetes management, yet current methodologies are constrained by resource intensiveness and methodological limitations. In vitro digestion models face challenges in replicating the dynamic conditions of the human gastrointestinal tract, such as enzyme variability and multi-time point analysis, leading to suboptimal predictive accuracy. This review proposes an integrated technological framework combining non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing with artificial intelligence to revolutionize GI assessment. Non-enzymatic sensors offer superior stability and repeatability in complex matrices, enabling real-time glucose quantification across multiple timepoints without enzyme degradation constraints. Machine learning algorithms, both supervised and unsupervised, enhance predictive accuracy by elucidating complex relationships within digestion data. This technological convergence represents a paradigm shift in food science analytics, promising improved throughput and precision in GI assessment. Future developments should focus on system scalability and broader applications across nutritional science, advancing diabetic management and personalized nutrition strategies.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Electrochemical sensor; Glycemic index; In vitro models; Starch hydrolysis.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Aderinola T., Ajayeoba T., Akanni G., Uzomah A., Onyeaka H., Adeboye A. Legume-based functional foods in West Africa for managing non-communicable diseases: A comprehensive review of dietary strategies. Nutrire. 2024;49(2):47. doi: 10.1186/s41110-024-00290-7. - DOI
-
- Afrose Subaitha Z., Priyadarshini S.R., Yoha K.S., Moses J.A. Impact of post-harvest processing techniques on the glycemic index of millets. Food Chemistry Advances. 2024;4 doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2024.100636. - DOI
-
- Ayranci R., Demirkan B., Sen B., Şavk A., Ak M., Şen F. Use of the monodisperse Pt/Ni@rGO nanocomposite synthesized by ultrasonic hydroxide assisted reduction method in electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose detection. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2019;99:951–956. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.02.040. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

