Nanosized MCM-41 silica from rice husk and its application for the removal of organic dyes from water
- PMID: 39867322
- PMCID: PMC11759526
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra07152b
Nanosized MCM-41 silica from rice husk and its application for the removal of organic dyes from water
Abstract
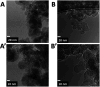
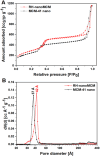
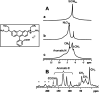
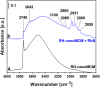
A novel synthesis of a nanometric MCM-41 from biogenic silica obtained from rice husk is here presented. CTABr and Pluronic F127 surfactants were employed as templating agents to promote the formation of a long-range ordered 2D-hexagonal structure with cylindrical pores and to limit the particle growth at the nanoscale level thus resulting in a material with uniform particle size of 20-30 nm. The physico-chemical properties of this sample (RH-nanoMCM) were investigated through a multi-technique approach, including PXRD, 29Si MAS NMR, TEM, Z-potential and N2 physisorption analysis at 77 K. The results were compared to those of a nanometric MCM-41 synthesized from a silicon alkoxide precursor. The adsorption capacity of RH-nanoMCM towards the cationic dye rhodamine B from aqueous phase was investigated at different initial dye concentrations by means of UV-vis spectroscopy. Insight into the non-covalent interactions between the dye molecules and the adsorbent surface was gained by means of 1H and 13C MAS NMR spectroscopy and FT-IR spectroscopy.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Photocatalytic removal of Congo red dye using MCM-48/Ni2O3 composite synthesized based on silica gel extracted from rice husk ash; fabrication and application.J Environ Manage. 2017 Dec 15;204(Pt 1):189-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.08.048. Epub 2017 Sep 4. J Environ Manage. 2017. PMID: 28881328
-
Novel acridone-modified MCM-41 type silica: Synthesis, characterization and fluorescence tuning.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2011;2:284-92. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.2.33. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21977441 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of Fe-MCM-41 from rice husk silica by hydrothermal technique for arsenate adsorption.Environ Geochem Health. 2010 Aug;32(4):261-6. doi: 10.1007/s10653-010-9292-z. Epub 2010 Apr 17. Environ Geochem Health. 2010. PMID: 20401518
-
Synthesis and characterization of a novel composite of rice husk-derived graphene oxide with titania microspheres (GO-RH/TiO2) for effective treatment of cationic dye methylene blue in aqueous solutions.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Sep;29(42):63917-63935. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20176-3. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35467189
-
Rice husk waste into various template-engineered mesoporous silica materials for different applications: A comprehensive review on recent developments.Chemosphere. 2023 Jan;310:136843. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136843. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Chemosphere. 2023. PMID: 36243081 Review.
References
-
- Khan D. Shaily Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2023;37:e7007.
-
- Mehmood A. Ghafar H. Yaqoob S. Gohar U. F. Ahmad B. J. Dev. Drugs. 2017;6(2) doi: 10.4172/2329-6631.1000174. - DOI
-
- Costa J. A. S. De Jesus R. A. Santos D. O. Mano J. F. Romão L. P. C. Paranhos C. M. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020;291:109698.
-
- Carniato F. Bisio C. Paul G. Gatti G. Bertinetti L. Coluccia S. Marchese L. J. Mater. Chem. 2010;20:5504.
-
- Li Z. Barnes J. C. Bosoy A. Fraser Stoddart J. Zink J. I. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012;41:2590–2605. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

