This is a preprint.
Large language models outperform traditional structured data-based approaches in identifying immunosuppressed patients
- PMID: 39867358
- PMCID: PMC11759841
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.16.25320564
Large language models outperform traditional structured data-based approaches in identifying immunosuppressed patients
Abstract
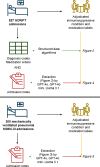
Identifying immunosuppressed patients using structured data can be challenging. Large language models effectively extract structured concepts from unstructured clinical text. Here we show that GPT-4o outperforms traditional approaches in identifying immunosuppressive conditions and medication use by processing hospital admission notes. We also demonstrate the extensibility of our approach in an external dataset. Cost-effective models like GPT-4o mini and Llama 3.1 also perform well, but not as well as GPT-4o.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics declarations Competing interests T.L.W. has received research funding from Gilead Sciences to support investigation of the relationship between immunosuppressive conditions and COVID-19 outcomes. Gilead personnel had no involvement in this research. All other authors declare no financial or non-financial competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- FastStats. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/pneumonia.htm (2024).
Publication types
Grants and funding
- R01 HL153122/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 LM014201/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI181102/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG075423/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL169815/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL154998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 TR003528/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM013337/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147575/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL149883/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL169188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 ES034350/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG079754/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL158139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD107571/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
