Overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism abnormality associated with SSRIs: a pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA adverse event reporting system
- PMID: 39867657
- PMCID: PMC11759304
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1517546
Overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism abnormality associated with SSRIs: a pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA adverse event reporting system
Abstract
Background: In the past few decades, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) became widely used antidepressants worldwide. Therefore, the adverse reactions of patients after SSRI administration became a public and clinical concern. In this study, we conducted a pharmacovigilance study using the Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database of the US Food and Drug Administration. Our main goal was to evaluate adverse events related to SSRIs, with a particular focus on abnormal weight gain and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders.
Method: The adverse event data for representative SSRIs (citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline) was extracted from the FAERS database from 2004Q1 to 2023Q4. The reporting odds ratio and proportional reporting ratio were employed to explore relevant adverse event reports (ADEs) signals. Univariate logistic regression analysis was utilized to explore factors associated with glucose/lipid metabolism abnormality following SSRIs treatment.
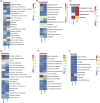
Results: We identified 143,744 ADE reports associated with SSRIs and revealed significant abnormal signals related to weight gain and glucose/lipid metabolism in depressed patients. Variations were observed among different SSRIs medications. Specifically, citalopram was associated with abnormal weight gain (ROR: 4, 95% CI: 3.1-5.2) and hepatic steatosis (ROR: 2.8, 95% CI: 2.1-3.6); escitalopram was correlated with gestational diabetes (ROR: 9.1, 95% CI: 6.6-12.4) and cholestasis (ROR: 2.4, 95% CI: 1.75-3.38); fluoxetine was associated with obesity (ROR: 2.8, 95% CI: 2.08-3.78); fluvoxamine was linked to arteriospasm coronary (ROR: 13.87, 95% CI: 4.47-43.1); and sertraline was implicated in neonatal jaundice (ROR: 16.1, 95% CI: 12.6-20.6). Females and younger age are important risk factors for the development of associated adverse effects.
Conclusion: Our study screened for adverse effects associated with abnormal glucose/lipid metabolism, such as abnormal body weight and fatty liver, in depressed patients taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors by utilizing FAERS database. This provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals in accepting and managing patients treated with SSRIs.
Keywords: ADEs; FAERS; glucose/lipid metabolism disorders; overweight; selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Chen, Wang, Ma, Yang, Cai, Xiao and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Focus on Abuse/Misuse and Withdrawal Issues with Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Analysis of Both the European EMA and the US FAERS Pharmacovigilance Databases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 1;15(5):565. doi: 10.3390/ph15050565. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631391 Free PMC article.
-
Safety Profile of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors in Real-World Settings: A Pharmacovigilance Study Based on FDA Adverse Event Reporting System.Ann Pharmacother. 2024 Nov;58(11):1105-1116. doi: 10.1177/10600280241231116. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Ann Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38407147
-
Exploring the association between selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and rhabdomyolysis risk based on the FDA pharmacovigilance database.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 28;13(1):12257. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39482-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37507539 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and guide to selection of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.Drugs. 1999 Apr;57(4):507-33. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199957040-00005. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10235690
-
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996 Dec;31(6):444-69. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199631060-00004. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996. PMID: 8968657 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of fluoxetine on body weight, waist circumference, and body mass index in individuals who are overweight or have obesity: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Obes (Lond). 2025 Aug 26. doi: 10.1038/s41366-025-01891-6. Online ahead of print. Int J Obes (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40858794 Review.
References
-
- Banzi R., Cusi C., Randazzo C., Sterzi R., Tedesco D., Moja L. (2015). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for the prevention of migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 4 (4), CD002919. 10.1002/14651858.CD002919.pub3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

