Microbiological Spectrum and Antibiotics Sensitivity Pattern of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) Patients: A prospective study from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Peshawar
- PMID: 39867757
- PMCID: PMC11755314
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.41.1.9992
Microbiological Spectrum and Antibiotics Sensitivity Pattern of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) Patients: A prospective study from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Peshawar
Abstract
Background & objective: Chronic suppurative otitis media is a fatal condition owing to its propensity for intracranial extension. The inadvertent use of antibiotics has led to resistance among causative organisms. The objectives of this study were to determine causative bacteria, their antibiotic resistance and susceptibility patterns, and their response to antibiotics after a one-month follow-up.
Method: It was a prospective study conducted in the ENT department of Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar from June 2023 to March 2024. Ear swabs were collected for microscopy and bacterial culture. Statistical analysis was done using IBM-SPSS-20, and GraphPad Prism.
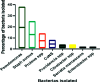
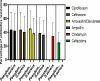
Results: Data was collected from 113 patients. The mean age of the patients was 22 + 2 years. Out of 113 samples, 97(85.5%) showed growth on culture whereas 16(14%) showed no growth, with 95 (98%) unimicrobial, while 2 (2%) showed polymicrobial growth. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was the commonest bacteria isolated 38(38%), followed by S. aureus, Proteus species, and S. saprophyticus. Gram-positive bacteria were susceptible to Linezolid (80%), followed by Vancomycin (76%), with resistance to Ciprofloxacin (75-84%), Ampicillin (70%), and Ceftriaxone (75-80%). Gram-negative bacteria showed susceptibility to carbapenem (50-100%) and Piperacillin/Tazobactam (50% to 93%), with resistance to Ciprofloxacin (50-87%), Ceftriaxone (87%), and Amoxicillin/Clavulanate (72-90%). After one month of follow-up, 82% of patients showed improvements, with noncompliance significantly associated with the persistence of symptoms (p<0.01).
Conclusion: Moderate to high resistance against ciprofloxacin, third-generation cephalosporin, ampicillin, amoxicillin plus clavulanate, and clindamycin is an eye-opener. Our results underscore the critical need for judicious administration of empirical antibiotics.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Antibiotic sensitivity; CSOM; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staph aureus.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microbiology of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: An update from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangladesh.Pak J Med Sci. 2021 May-Jun;37(3):821-826. doi: 10.12669/pjms.37.3.3942. Pak J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34104172 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiological profile with antibiotic sensitivity pattern of cholesteatomatous chronic suppurative otitis media among children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011 Sep;75(9):1104-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.05.025. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011. PMID: 21715027
-
Bacteriological Profile of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media and Antibiotic Susceptibility in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Shanghai, China.Ear Nose Throat J. 2021 Nov;100(9):NP391-NP396. doi: 10.1177/0145561320923823. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021. PMID: 32352873
-
Analysis of main pathogenic bacteria and drug sensitivity in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media and middle ear cholesteatoma in China.Biotechnol Lett. 2020 Aug;42(8):1559-1566. doi: 10.1007/s10529-020-02880-7. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Biotechnol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32270423
-
Literature review on the distribution characteristics and antimicrobial resistance of bacterial pathogens in neonatal sepsis.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Mar;35(5):861-870. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1732342. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022. PMID: 32102584 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
