Active Ingredients and Potential Mechanism of Additive Sishen Decoction in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis with Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experimental Verification
- PMID: 39867868
- PMCID: PMC11762093
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S489323
Active Ingredients and Potential Mechanism of Additive Sishen Decoction in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis with Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experimental Verification
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease in which macrophages produce cytokines that enhance inflammation and contribute to the destruction of cartilage and bone. Additive Sishen decoction (ASSD) is a widely used traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of RA; however, its active ingredients and the mechanism of its therapeutic effects remain unclear.
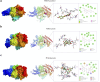
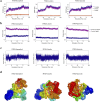
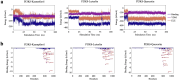
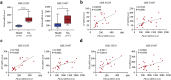
Methods: To predict the ingredients and key targets of ASSD, we constructed "drug-ingredient-target-disease" and protein-protein interaction networks. Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analyses were performed to explore the potential mechanism. The activity of the predicted key ingredients was verified in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. The binding mode between the key ingredients and key targets was elucidated using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation.
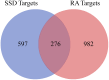
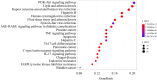
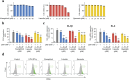
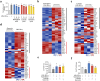
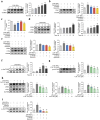
Results: In all, 75 ASSD active ingredients and 1258 RA targets were analyzed, of which kaempferol, luteolin, and quercetin were considered key components that mainly act through inflammation-related pathways, such as the PI3K-AKT, TNF, and IL-17 signaling pathways, to ameliorate RA. Transcriptome sequencing suggested that kaempferol-, luteolin-, and quercetin-mediated inhibition of glycolysis reduced the lipopolysaccharide-induced production of proinflammatory factors. In vitro experiments indicated that kaempferol, luteolin, and quercetin decreased Glut1 and LDHA expression by diminishing PI3K-AKT signaling to inhibit glycolysis. Molecular dynamic simulation revealed that kaempferol, luteolin, and quercetin stably occupied the hydrophobic pocket of PI3Kδ.
Conclusion: Our results show that the PI3Kδ-mediated anti-inflammatory responses elicited by kaempferol, luteolin, and quercetin are crucial for the therapeutic efficacy of ASSD against RA.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; PI3K-AKT; glycolysis; inflammation; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2025 Ren et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of Siegesbeckia orientalis L. and its active compound luteolin in rheumatoid arthritis: network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116852. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116852. Epub 2023 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37390879
-
Exploring the mechanism of Xiaoqinglong decoction in the treatment of infantile asthma based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jan 13;102(2):e32623. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032623. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36637916 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the potential mechanism of Yiyi Tongfeng Formula in the treatment of acute gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 13;103(37):e39609. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039609. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39287271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wutou decoction: A latest review on molecular mechanisms, clinical studies, quality control, pharmacokinetic studies, pharmacological effects, toxicity, and target prediction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 11;341:119307. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119307. Epub 2024 Dec 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39743182 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Di-(2-Ethylhexyl)-Phthalate on Metabolic Syndrome: Insights from Network Toxicology and Molecular Docking and Dynamics.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Jul 8;18:2277-2288. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S523668. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40655169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janossy G, Panayi G, Duke O, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981;2:839–842. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

