Higher monomeric C-reactive protein levels are associated with premature coronary artery disease
- PMID: 39867895
- PMCID: PMC11757105
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501125
Higher monomeric C-reactive protein levels are associated with premature coronary artery disease
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic inflammation is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD). Currently, the inflammatory cardiovascular risk is assessed via C-reactive protein (CRP) levels measured using a high-sensitivity assay (hsCRP). Monomeric CRP (mCRP) is a locally produced form of CRP that has emerged as a potential biomarker of inflammation.
Aim: This study investigated whether mCRP levels are associated with premature CAD.
Materials and methods: This study comprised 103 participants of both sexes, including 50 patients 56 ± 7 years old with premature CAD and 53 patients 51 ± 10 years old without CAD. CAD was verified using coronary angiography, hsCRP levels were measured using a standard assay, and mCRP levels were measured using fluorescent cytometric beads conjugated with an anti-mCRP antibody.
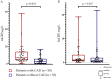
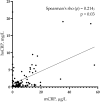
Results: The levels of hsCRP were 0.99 (0.59; 3.10) mg/L vs. 0.63 (0.35; 1.85) mg/L (p = 0.067), and mCRP 6.84 (4.20; 13.78) µg/L vs. 2.57 (0.32; 5.66) µg/L (p <0.001) in patients with CAD vs. patients without CAD, respectively. There was a weak positive correlation between the mCRP and hsCRP levels (ρ = 0.214; p = 0.030). hsCRP levels were below 2.0 mg/L (i.e., residual inflammatory cardiovascular risk should have been excluded) in 70% of patients with CAD and 79% of patients without CAD (p = 0.365). mCRP levels differed between the groups of patients with hsCRP levels below 2.0 mg/L: 5.14 (4.07; 10.68) µg/L vs. 2.77 (0.53; 5.00) µg/L in patients with or without CAD, respectively (p <0.001). Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that mCRP levels were independently associated with premature CAD. The adjusted odds ratio was 1.18 (95% CI 1.06-1.33, p = 0.004) per each µg/L increase in mCRP levels.
Conclusion: Higher mCRP levels were associated with premature CAD, independent of hsCRP levels and traditional risk factors.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; atherosclerosis; coronary artery disease; inflammation; mCRP; monomeric C-reactive protein; residual inflammatory cardiovascular risk.
Copyright © 2025 Melnikov, Kozlov, Okhota, Saburova, Avtaeva, Kuznetsova, Guria, Prokofieva, Riazantseva, Ji, Wu and Gabbasov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

