This is a preprint.
Development of FAP-targeted theranostics discovered by next-generation sequencing-augmented mining of a novel immunized VNAR library
- PMID: 39868181
- PMCID: PMC11761682
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.13.632555
Development of FAP-targeted theranostics discovered by next-generation sequencing-augmented mining of a novel immunized VNAR library
Abstract
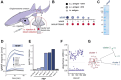
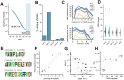
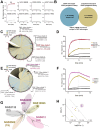
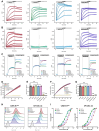
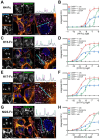
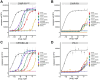
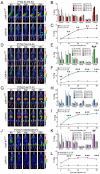
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the stroma of solid tumors promote an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) that drives resistance to therapies. The expression of the protease fibroblast activation protein (FAP) on the surface of CAFs has made FAP a target for development of therapies to dampen immunosuppression. Relatively few biologics have been developed for FAP and none have been developed that exploit the unique engagement properties of Variable New Antigen Receptors (VNARs) from shark antibodies. As the smallest binding domain in nature, VNARs cleverage unique geometries and recognize epitopes conventional antibodies cannot. By directly immunizing a nurse shark with FAP, we created a large anti-FAP VNAR phage display library. This library allowed us to identify a suite of anti-FAP VNARs through traditional biopanning and also by an in silico approach that did not require any prior affinity-based enrichment in vitro. We investigated four VNAR-Fc fusion proteins for theranostic properties and found that all four recognized FAP with high affinity and were rapidly internalized by FAP-positive cells. As a result, the VNAR-Fc constructs were effective antibody-drug conjugates in vitro and were able to localize to FAP-positive xenografts in vivo. Our findings establish VNAR-Fc constructs as a versatile platform for theranostic development that could yield innovative cancer therapies targeting the TME.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The characterization of variable new antigen receptors targeting FAP isolated from a novel immunized library.Commun Biol. 2025 Aug 13;8(1):1210. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08610-x. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40804296 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and next-generation sequencing analysis of a large phage-displayed VNAR single-domain antibody library from six naïve nurse sharks.Antib Ther. 2019 Jan;2(1):1-11. doi: 10.1093/abt/tby011. Epub 2018 Nov 7. Antib Ther. 2019. PMID: 30627698 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring shark VNAR antibody against infectious diseases using phage display technology.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Sep;140:108986. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108986. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37541634 Review.
-
Ancient species offers contemporary therapeutics: an update on shark VNAR single domain antibody sequences, phage libraries and potential clinical applications.Antib Ther. 2020 Jan;3(1):1-9. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbaa001. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Antib Ther. 2020. PMID: 32118195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel shark VNAR antibody-based immunotoxin targeting TROP-2 for cancer therapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Nov;14(11):4806-4818. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.08.023. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39664437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taylor R.A. & Risbridger G.P. Prostatic tumor stroma: a key player in cancer progression. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8, 490–497 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
