This is a preprint.
Structural mechanism for recognition of E2F1 by the ubiquitin ligase adaptor Cyclin F
- PMID: 39868286
- PMCID: PMC11761524
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.15.633208
Structural mechanism for recognition of E2F1 by the ubiquitin ligase adaptor Cyclin F
Update in
-
Structural mechanism for the recognition of E2F1 by the ubiquitin ligase adaptor Cyclin F.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul;122(26):e2501057122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2501057122. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40549918
Abstract
Cyclin F, a non-canonical member of the cyclin protein family, plays a critical role in regulating the precise transitions of cell-cycle events. Unlike canonical cyclins, which bind and activate cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), Cyclin F functions as a substrate receptor protein within the Skp1-Cullin-F box (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, enabling the ubiquitylation of target proteins. The structural features that distinguish Cyclin F as a ligase adaptor and the mechanisms underlying its selective substrate recruitment over Cyclin A, which functions in complex with CDK2 at a similar time in the cell cycle, remain largely unexplored. We utilized single-particle cryo-electron microscopy to elucidate the structure of a Cyclin F-Skp1 complex bound to an E2F1 peptide. The structure and biochemical analysis reveal important differences in the substrate-binding site of Cyclin F compared to Cyclin A. Our findings expand on the canonical cyclin-binding motif (Cy or RxL) and highlight the importance of electrostatics at the E2F1 binding interface, which varies for Cyclin F and Cyclin A. Our results advance our understanding of E2F1 regulation and may inform the development of inhibitors targeting Cyclin F.
Figures



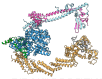
References
-
- Galper J. et al. , Cyclin F: A component of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex with roles in neurodegeneration and cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 89, 216–220 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
