This is a preprint.
Dimerization and dynamics of angiotensin-I converting enzyme revealed by cryo-EM and MD simulations
- PMID: 39868314
- PMCID: PMC11760429
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.09.632263
Dimerization and dynamics of angiotensin-I converting enzyme revealed by cryo-EM and MD simulations
Abstract
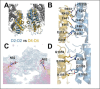
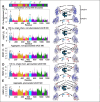
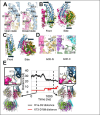
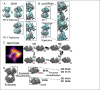
Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) regulates the levels of disparate bioactive peptides, notably converting angiotensin-I to angiotensin-II and degrading amyloid beta. ACE is a heavily glycosylated dimer, containing 4 analogous catalytic sites, and exists in membrane bound and soluble (sACE) forms. ACE inhibition is a frontline, FDA-approved, therapy for cardiovascular diseases yet is associated with significant side effects, including higher rates of lung cancer. To date, structural studies have been confined to individual domains or partially denatured cryo-EM structures. Here we report the cryo-EM structure of the glycosylated full sACE dimer. We resolved four structural states at 2.99 to 3.65 Å resolution which are primarily differentiated by varying degrees of solvent accessibility to the active sites and reveal the full dimerization interface. We also employed all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and heterogeneity analysis in cryoSPARC, cryoDRGN, and RECOVAR to elucidate the conformational dynamics of sACE and identify key regions mediating conformational change. We identify differences in the mechanisms governing the conformational dynamics of individual domains that have implications for the design of domain-specific sACE modulators.
Keywords: Angiotensin-I converting enzyme; all-atom MD simulations; amyloid peptide; cryo-EM; hypertension.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for adults with early (stage 1 to 3) non-diabetic chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 19;7(7):CD007751. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007751.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37466151 Free PMC article.
-
Brexanolone, zuranolone and related neurosteroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators for postnatal depression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 26;6(6):CD014624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014624.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40562419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Aug 22;2014(8):CD009096. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009096.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25148386 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 5;4(4):CD007066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007066.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28379619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Turner A. J., Hooper N. M., The angiotensin-converting enzyme gene family: genomics and pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23, 177–183 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Herman L. L., Padala S. A., Ahmed I., Bashir K., “Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEI)” in StatPearls. (Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Sandeep Padala declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Intisar Ahmed declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Khalid Bashir declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies., 2024).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
