Interpretable machine learning models for predicting skip metastasis in cN0 papillary thyroid cancer based on clinicopathological and elastography radiomics features
- PMID: 39868368
- PMCID: PMC11758178
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1457660
Interpretable machine learning models for predicting skip metastasis in cN0 papillary thyroid cancer based on clinicopathological and elastography radiomics features
Abstract
Background: Skip lymph node metastasis (SLNM) in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) involves cancer cells bypassing central nodes to directly metastasize to lateral nodes, often undetected by standard preoperative ultrasonography. Although multiple models exist to identify SLNM, they are inadequate for clinically node-negative (cN0) patients, resulting in underestimated metastatic risks and compromised treatment effectiveness. Our study aims to develop and validate a machine learning (ML) model that combines elastography radiomics with clinicopathological data to predict pre-surgical SLNM risk in cN0 PTC patients with increased risk of lymph node metastasis (LNM), improving their treatment strategies.
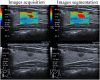
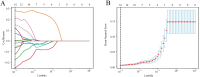
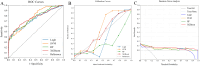
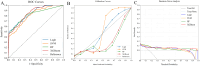
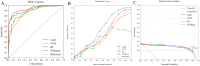
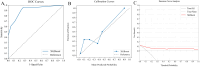
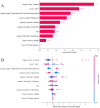
Methods: Our study conducted a retrospective analysis of 485 newly diagnosed primary PTC patients, divided into training and external validation cohorts. Patients were categorized into SLNM and non-SLNM groups based on follow-up outcomes and postoperative pathology. We collected preoperative clinicopathological data and extracted, standardized radiomics features from elastography imaging to develop various ML models. These models were internally validated using radiomics and clinicopathological data, with the optimal model's feature importance analyzed through the Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) approach and subsequently externally validated.
Results: In our study of 485 patients, 67 (13.8%) exhibited SLNM. The extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model, integrating elastography radiomics with clinicopathological data, demonstrated superior performance in both internal and external validations. SHAP analysis identified five key determinants of SLNM: three radiomics features from elastography images, one clinical variable, and one pathological variable.
Conclusion: Our evaluation highlights the XGBoost model, which integrates elastography radiomics and clinicopathological data, as the most effective ML approach for the prediction of SLNM in cN0 PTC patients with increased risk of LNM. This innovative model significantly enhances the accuracy of risk assessments for SLNM, enabling personalized treatments that could reduce postoperative metastases in these patients.
Keywords: clinically node-negative (cN0); machine learning; papillary thyroid cancer; radiomics; skip lymph node metastasis.
Copyright © 2025 Yao, Tang, Lu, Zhou and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nomogram for predicting skip metastasis in cN0 papillary thyroid cancer patients at increased risk of lymph node metastasis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2023 Jul;32(7):753-761. doi: 10.17219/acem/157240. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36603142
-
Prediction of lateral lymph node metastasis with short diameter less than 8 mm in papillary thyroid carcinoma based on radiomics.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Nov 15;24(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00803-7. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39548590 Free PMC article.
-
[Preoperative Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Combined With Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma Using Machine Learning and Radiomics-Based Features: A Preliminary Study].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jul 20;55(4):1026-1033. doi: 10.12182/20240760605. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39170022 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Machine Learning Model for Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinically Node Positive Breast Cancer Based on Peritumoral Ultrasound Radiomics and SHAP Feature Analysis.J Ultrasound Med. 2024 Sep;43(9):1611-1625. doi: 10.1002/jum.16483. Epub 2024 May 29. J Ultrasound Med. 2024. PMID: 38808580
-
The Prognosis of Skip Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma Is Better Than That of Continuous Metastasis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 May 17;107(6):1589-1598. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac107. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35213704 Review.
References
-
- Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. . 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American thyroid association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. (2016) 26:1–133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

