Botensilimab (Fc-enhanced anti-cytotoxic lymphocyte-association protein-4 antibody) Plus Balstilimab (anti-PD-1 antibody) in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Metastatic Sarcomas
- PMID: 39869830
- PMCID: PMC11974637
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-24-02524
Botensilimab (Fc-enhanced anti-cytotoxic lymphocyte-association protein-4 antibody) Plus Balstilimab (anti-PD-1 antibody) in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Metastatic Sarcomas
Abstract
Purpose: Outcomes for patients with advanced sarcomas are poor and there is a high unmet need to develop novel therapies. The purpose of this phase I study was to define the safety and efficacy of botensilimab (BOT), an Fc-enhanced anti-cytotoxic lymphocyte-association protein-4 antibody, plus balstilimab (BAL), an anti-PD-1 antibody, in advanced sarcomas.
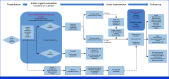
Methods: BOT was administered intravenously (IV) at 1 mg/kg or 2 mg/kg once every 6 weeks in combination with BAL IV at 3 mg/kg once every 2 weeks for up to 2 years. The primary end point was to determine dose-limiting toxicities during the dose-escalation period. Secondary end points include objective response rate (ORR), duration of response (DOR), disease control rate, and progression-free survival (PFS) by RECIST 1.1. Exploratory end points include assessing patient biomarkers including tumor mutational burden, cytokines, and PD-L1 expression.
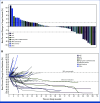
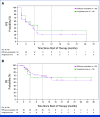
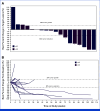
Results: Overall, 64 patients with sarcoma were treated; all were evaluable for safety and 52 for efficacy. The most common treatment-related adverse event (TRAE) was diarrhea/colitis occurring in 35.9% of patients, with grade 3 in 6.3% of patients. No grade 4 or 5 TRAEs were reported. For all evaluable patients, ORR was 19.2% (95% CI, 9.6 to 32.5), and 27.8% (95% CI, 9.7 to 53.5) for evaluable patients with angiosarcoma (n = 18); 33.3% in visceral and 22.2% in cutaneous subtypes. Median PFS for evaluable patients was 4.4 months (95% CI, 2.8 to 6.1), with a 6-month PFS rate of 36% (95% CI, 22 to 50) and a median DOR of 21.7 months (95% CI, 1.9 to not reached).
Conclusion: The combination of BOT/BAL demonstrated promising efficacy and safety in a large cohort of heavily pretreated sarcoma patients. This encouraging activity warrants further investigation (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03860272).
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board : Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours (ed 5). Lyon, France, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2020
-
- SEER*Explorer : An interactive website for SEER cancer statistics. Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute, 2023. https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/
-
- Petitprez F, de Reynies A, Keung EZ, et al. : B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma. Nature 577:556-560, 2020 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

