A Spiropyran-Based Hydrogel Composite for Wearable Detectors to Monitor Visible Light Intensity to Prevent Myopia
- PMID: 39869852
- PMCID: PMC11803555
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5c00250
A Spiropyran-Based Hydrogel Composite for Wearable Detectors to Monitor Visible Light Intensity to Prevent Myopia
Abstract
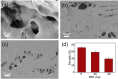
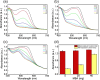
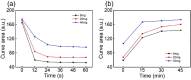
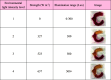
A wearable detector to monitor visible light intensity is realized by the restrained photochromism of a hydrogel composite containing light-responsive spiropyran with hydroxyl groups (SPOH). When exposed to visible light, the SPOH experiences a ring-opening to a ring-closed transition accompanied by discoloration from red to yellow. Unlike in the solution, the photochromism/discoloration rate is strongly correlated to the cross-linking points. By reducing the amount of cross-linker from 40 to 5 mg, the photochromism rate of SPOH is 300% faster. Inspired by the Chinese Jade Loong from Hongshan, the hydrogel composite is shaped into a Loong to monitor the light intensity. By increasing the amount of cross-linker in the head, body, and tail, the photochromism/discoloration rate sequentially turns slower from one region to the other. Higher light intensity is required to realize the discoloration in the hydrogel composite containing a larger amount of the cross-linker. Because the initial colors are identical, the light intensity can be easily traced by checking the discoloration of these pieces containing different amounts of cross-linker. Based on this unique and reversible photochromic capability, the present hydrogel composite can be used for monitoring the visible light intensity to prevent myopia, especially for children and students.
Keywords: hydrogel composites; myopia prevention; reversible photochromism; spiropyran; visible light detector.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multi-responsive supramolecular hydrogels based on merocyanine-peptide conjugates.Org Biomol Chem. 2015 Dec 21;13(47):11492-8. doi: 10.1039/c5ob01912e. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Org Biomol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26456175
-
A photo-switchable and thermal-enhanced fluorescent hydrogel prepared from N-isopropylacrylamide with water-soluble spiropyran derivative.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018 Sep;29(13):1579-1594. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2018.1475942. Epub 2018 Jun 1. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018. PMID: 29792381
-
Photoresponsive Passive Micromixers Based on Spiropyran Size-Tunable Hydrogels.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2018 Jan;39(1). doi: 10.1002/marc.201700086. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2018. PMID: 28418112
-
Chemo- and biosensing applications of spiropyran and its derivatives - A review.Anal Chim Acta. 2020 May 8;1110:199-223. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.01.057. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Anal Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32278396 Review.
-
A Modern Look at Spiropyrans: From Single Molecules to Smart Materials.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2023 Jan 10;381(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s41061-022-00417-2. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2023. PMID: 36624333 Review.
References
-
- St-Jean P.; Clark O. G.; Jemtrud M. A Review of the Effects of Architectural Stimuli on Human Psychology and Physiology. Build. Environ 2022, 219, 109182.10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109182. - DOI
-
- Wang Y.; Zhong X.; Zhang Y.; Tu Y.; Wang L.; Chen Y.; Zhang C.; Zhou W. Visual Fatigue Following Long-term Visual Display Terminal Work under Different Light Sources. Lighting Res. Technol 2017, 49, 1034–1051. 10.1177/1477153516677559. - DOI
-
- Kalra P.; Karar V. Effect of Screen Switching and Brightness on Visual Fatigue in AR Environments. IETE Tech Rev 2023, 40, 303–311. 10.1080/02564602.2022.2100493. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

